Phylogeny and the Tree of LifePage
1
1
Slide 1
Investigating the Tree of Life
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species.
The discipline of systematics classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships.
Systematists use fossil, molecular, and genetic data to infer evolutionary relationships.
Taxonomy is the ordered division and naming of organisms.
Slide 2
Binomial Nomenclature
In the 18th century, Carolus Linnaeus published a system of taxonomy based on resemblances.
The two-part scientific name: Genus species.
The first letter of the genus is capitalized, and the entire species name is italicized
Both parts together name the species. This is the species specific epithet.
Slide 3
Hierarchical Classification
Linnaeus introduced a system for grouping species in increasingly broad categories.
The taxonomic groups from broad to narrow are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
A taxonomic unit at any level of hierarchy is called a taxon.
Slide 4
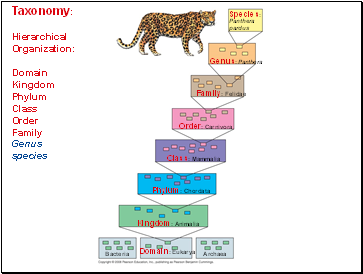
Taxonomy: Hierarchical Organization: Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species
Species:
Panthera
pardus
Genus: Panthera
Family: Felidae
Order: Carnivora
Class: Mammalia
Phylum: Chordata
Kingdom: Animalia
Archaea
Domain: Eukarya
Bacteria
Slide 5
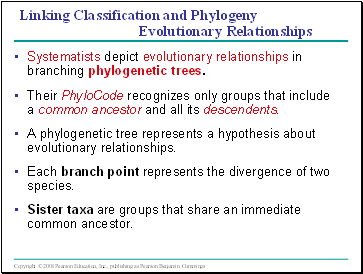
Linking Classification and Phylogeny Evolutionary Relationships
Systematists depict evolutionary relationships in branching phylogenetic trees.
Their PhyloCode recognizes only groups that include a common ancestor and all its descendents.
A phylogenetic tree represents a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships.
Each branch point represents the divergence of two species.
Sister taxa are groups that share an immediate common ancestor.
Slide 6
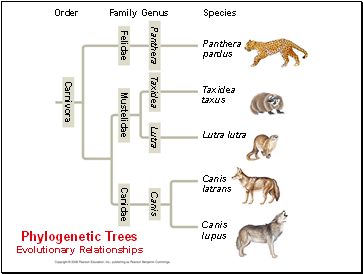
Species
Canis
lupus
Pantherapardus
Taxidea
taxus
Lutra lutra
Canis
latrans
Order
Family
Genus
Carnivora
Felidae
Mustelidae
Canidae
Canis
Lutra
Taxidea
Panthera
Phylogenetic Trees
Evolutionary Relationships
Slide 7
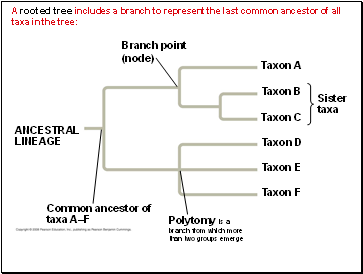
A rooted tree includes a branch to represent the last common ancestor of all taxa in the tree:
Sister
taxa
ANCESTRAL
LINEAGE
Taxon A
Polytomy is a branch from which more than two groups emerge
Contents
- Investigating the Tree of Life
- Binomial Nomenclature
- Hierarchical Classification
- Linking Classification and Phylogeny Evolutionary Relationships
- What We Can and Cannot Learn from Phylogenetic Trees
- Cladistics groups organisms by common descent
- Shared Ancestral and Shared Derived Characters
- Molecular Clocks
- Applying a Molecular Clock: The Origin of HIV
Last added presentations
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Friction
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Sound
- Upcoming Classes