Conservation Biology and Restoration EcologyPage
3
3
The small-population approach
The declining-population approach
Slide 18
Small-Population Approach
The small-population approach studies processes that can make small populations become extinct.
A small population is prone to positive-feedback loops that draw it down an extinction vortex.
The key factor driving the extinction vortex is loss of the genetic variation necessary to enable evolutionary responses to environmental change.
Slide 19
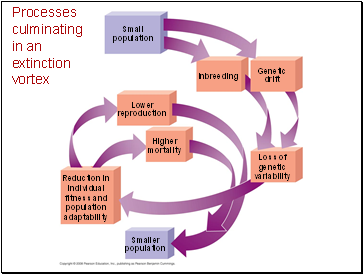
Processes culminating in an extinction vortex
Inbreeding
Small
population
Genetic
drift
Lower
reproduction
Higher
mortality
Smaller
population
Reduction in
individual
fitness and
population
adaptability
Loss of
genetic
variability
Slide 20
Minimum Viable Population Size
Minimum viable population MVP is the minimum population size at which a species can survive.
The MVP depends on factors that affect a populationís chances for survival over a particular time.
A meaningful estimate of MVP requires determining the effective population size, which is based on the populationís breeding potential.
Slide 21
Case Study: Analysis of Grizzly Bear Populations
One of the first population viability analyses was conducted as part of a long-term study of grizzly bears in Yellowstone National Park.
This grizzly population is about 400, but the Ne is about 100.
The Yellowstone grizzly population has low genetic variability compared with other grizzly populations.
Introducing individuals from other populations would increase the numbers and genetic variation.
Slide 22
Long-term monitoring of a grizzly bear population
Slide 23
Declining-Population Approach
The declining-population approach
Focuses on threatened and endangered populations that show a downward trend, regardless of population size.
Emphasizes the environmental factors that caused a population to decline.
Slide 24
Steps for Analysis and Intervention
The declining-population approach involves several steps:
Confirm that the population is in decline
Study the speciesí natural history
Develop hypotheses for all possible causes of decline
Test the hypotheses in order of likeliness
Apply the results of the diagnosis to manage for recovery.
Contents
- Striking Gold
- Human activities threaten Earthís biodiversity
- Three Levels of Biodiversity
- Biodiversity and Human Welfare
- Three Threats to Biodiversity
- Small-Population Approach
- Declining-Population Approach
- Weighing Conflicting Demands
- Landscape and regional conservation aim to sustain entire biotas
- Establishing Protected Areas
- Restoration ecology attempts to restore degraded ecosystems to a more natural state
- Bioremediation
- Biological Augmentation
- Sustainable development seeks to improve the human condition while conserving biodiversity
- The Future of the Biosphere
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- Thermal Energy
- Newtonís law of universal gravitation
- Friction
- Solar Energy
- Radiation
- Space Radiation