Curved MirrorsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Curved Mirrors
What are some examples of curved mirrors?
Slide 2
Concave Spherical Mirrors
A spherical mirror has the shape of part of a sphere’s surface.
Concave Spherical Mirror (Converging Mirror): A spherical mirror with light reflecting from its silvered, concave surface
Concave mirrors are used whenever a magnified image of an object is needed
Slide 3
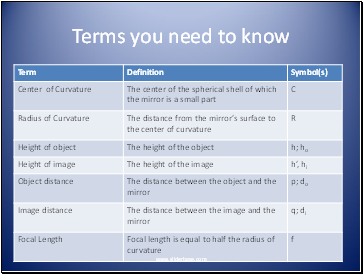
Terms you need to know
Slide 4
Concave Spherical Mirrors (p.531)
A spherical mirror is represented as a shell of a sphere
Slide 5
Concave Mirror (p.531)
Slide 6
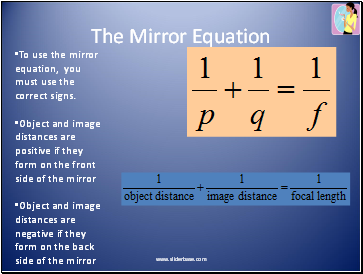
The Mirror Equation
To use the mirror equation, you must use the correct signs.
Object and image distances are positive if they form on the front side of the mirror
Object and image distances are negative if they form on the back side of the mirror
Slide 7
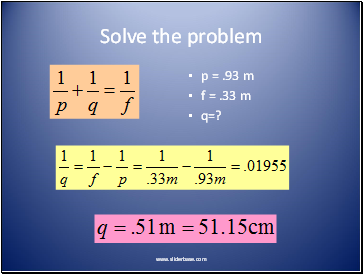
Sample Problem (p.536 #2)
A concave shaving mirror has a focal length of 33 cm. Calculate the image position of a cologne bottle placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 93 cm.
Slide 8
Solve the problem
p = .93 m
f = .33 m
q=?
Slide 9
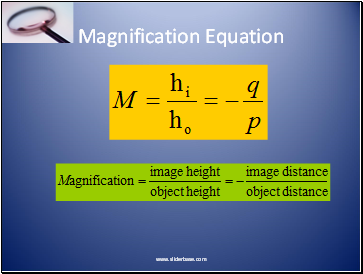
Magnification Equation
Slide 10
Sample Problem (p.536 #2)
A concave shaving mirror has a focal length of 33 cm. Calculate the magnification of the image. Is the image real or virtual? Is the image inverted or upright?
Slide 11
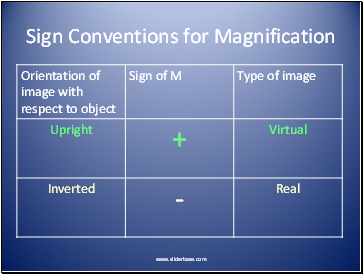
Sign Conventions for Magnification
Slide 12
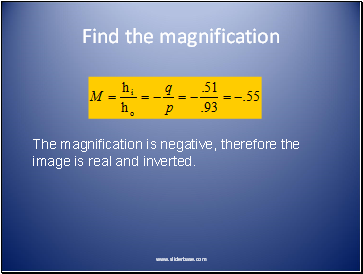
Find the magnification
The magnification is negative, therefore the image is real and inverted.
Slide 13
Ray Diagrams
A ray diagram is a drawing that uses geometry to locate an image formed by a mirror.
There are different rules for drawing ray diagrams depending on the type of mirror you have.
Slide 14
Contents
- Curved Mirrors
- Concave Spherical Mirrors
- The Mirror Equation
- Sample Problem (p.536 #2)
- Ray Diagrams
- Ray diagrams for convex mirrors
- Drawing the reference rays
- Convex Spherical Image Formation
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Buoyancy
- Waves & Sound
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Sound