Health PhysicsPage
4
4
A typical gamma camera is 40 cm in diameter – large enough to examine body tissues or specific organs. The gamma rays are given off in all directions but only the ones which travel towards the gamma camera will be detected.
Slide 25
The Gamma Camera
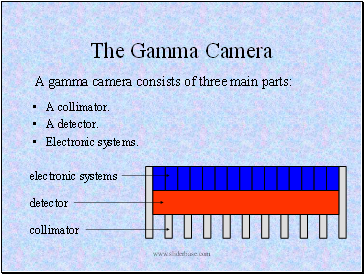
A collimator.
A detector.
Electronic systems.
A gamma camera consists of three main parts:
electronic systems
detector
collimator
Slide 26
The Gamma Camera
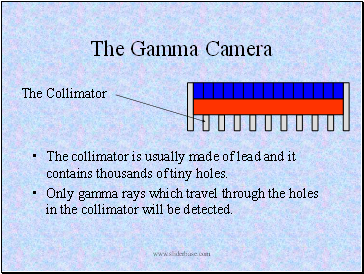
The collimator is usually made of lead and it contains thousands of tiny holes.
Only gamma rays which travel through the holes in the collimator will be detected.
The Collimator
Slide 27
The Gamma Camera
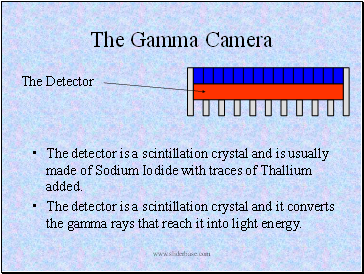
The detector is a scintillation crystal and is usually made of Sodium Iodide with traces of Thallium added.
The detector is a scintillation crystal and it converts the gamma rays that reach it into light energy.
The Detector
Slide 28
The Gamma Camera
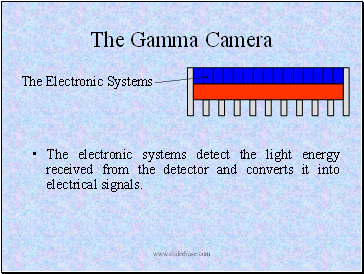
The electronic systems detect the light energy received from the detector and converts it into electrical signals.
The Electronic Systems
Slide 29
Diagnosis Static Imaging
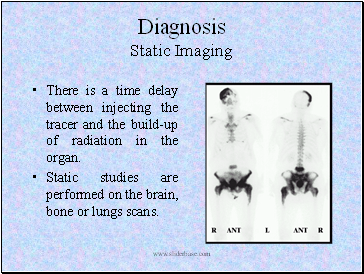
There is a time delay between injecting the tracer and the build-up of radiation in the organ.
Static studies are performed on the brain, bone or lungs scans.
Slide 30
Diagnosis Dynamic Imaging
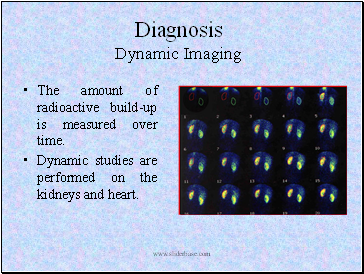
The amount of radioactive build-up is measured over time.
Dynamic studies are performed on the kidneys and heart.
Slide 31
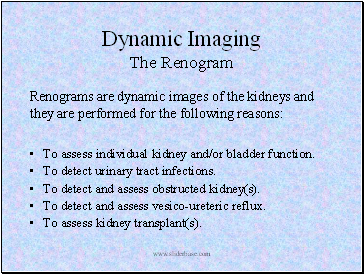
Dynamic Imaging The Renogram
To assess individual kidney and/or bladder function.
To detect urinary tract infections.
To detect and assess obstructed kidney(s).
To detect and assess vesico-ureteric reflux.
To assess kidney transplant(s).
Renograms are dynamic images of the kidneys and they are performed for the following reasons:
Slide 32
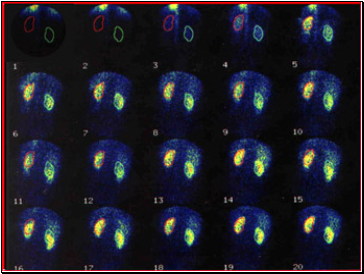
Performing the Renogram
The tracer is injected into the patient.
The radioactive material is removed from the bloodstream by the kidneys.
Within a few minutes of the injection, the radiation is concentrated in the kidneys.
After 10 – 15 minutes, almost all of the radiation should be in the bladder.
The gamma camera takes readings every few seconds for 20 minutes.
Slide 33
Contents
- What is Cancer?
- Treatment of Cancer
- The Aims of Radiation Therapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Radiotherapy Treatment Planning
- Radiotherapy Treatment
- Treatment of Cancer
- Tracers
- Nuclear Medicine Tracers
- The Gamma Camera
- Diagnosis Static Imaging
- Performing the Renogram
- Diagnosis The Renogram
- Sterilisation
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Newton's laws of motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Mechanics Lecture
- Health Physics
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations