MineralsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Minerals are naturally-occurring inorganic substances with a definite and predictable chemical composition and physical properties
Slide 2
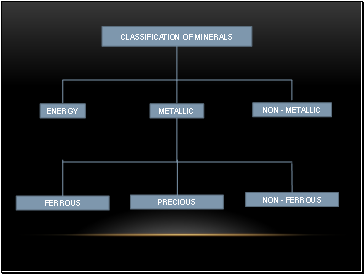
Classification of Minerals
Metallic Ferrous
Non-ferrous
Precious
Non-metallic
Energy Minerals
Slide 3
CLASSIFICATION OF MINERALS
METALLIC
ENERGY
NON - METALLIC
FERROUS
PRECIOUS
NON - FERROUS
Slide 4
Ferrous Iron Ore, Manganese, Nickel, Cobalt
Non-ferrous Copper, Lead, Tin, Bauxite
Precious Gold, Silver, Platinum
Non-metallic Mica, Salt, Potash, Sulphur
Energy Minerals Coal, Petroleum, Natural Gas
Slide 5
Ore
A mineral or an aggregate of minerals from which a valuable constituent, especially a metal, can be profitably mined or extracted
Slide 6
All Minerals are Ore
but
All Ore are not Minerals
Slide 7
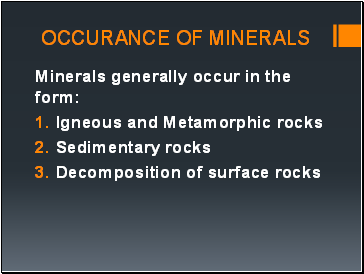
Occurance of minerals
Minerals generally occur in the form:
Igneous and Metamorphic rocks
Sedimentary rocks
Decomposition of surface rocks
Slide 8
Iron
Iron Ore is the basic mineral and is the backbone of Industrial development. Magnetite is the finest iron ore with a very high content of iron. Hematite ore is the most important industrial iron ore.
Slide 9
Metallurgy of Iron
Iron is found in great abundance in nature. It is highly reactive and is hardly available in free state. Iron exists in the combined form in nature in various minerals among which oxide and sulphide ores of iron are vastly used.
Slide 10
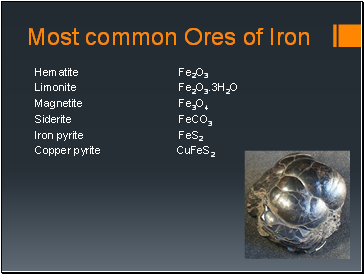
Most common Ores of Iron
Hematite Fe2O3
Limonite Fe2O3.3H2O
Magnetite Fe3O4
Siderite FeCO3
Iron pyrite FeS2
Copper pyrite CuFeS2
Slide 11
Metallurgy
Dressing of ore
pulverization
Concentration of ore
removal of moisture, volatile impurities
converting sulphur, phosphorus into their oxides
converting ferrous to ferric oxide
Reduction of ore
smelting
Slide 12
1 2
Contents
- Classification of Minerals
- Ore
- Occurance of minerals
- Iron
- Metallurgy of Iron
- Most common Ores of Iron
- Metallurgy
- Manganese
- Ores of manganeese
- Metallurgy of manganese
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Newtons law of universal gravitation
- Waves & Sound
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation