Homeostasis of the bodyPage
2
2
Slide 12
What mechanisms are there to cool the body down?
Vasodilation
Your blood carries most of the heat energy around your body.
There are capillaries underneath your skin that can be filled with blood if you get too hot.
This brings the blood closer to the surface of the skin so more heat can be lost.
This is why you look red when you are hot!
Slide 13
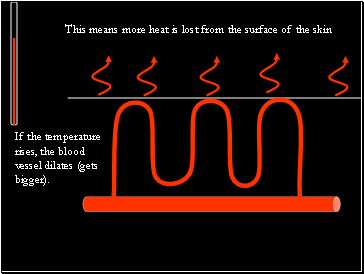
If the temperature rises, the blood vessel dilates (gets bigger).
This means more heat is lost from the surface of the skin
Slide 14
What mechanisms are there to warm the body up?
Vasoconstriction
This is the opposite of vasodilation
The capillaries underneath your skin get constricted (shut off).
This takes the blood away from the surface of the skin so less heat can be lost.
Slide 15
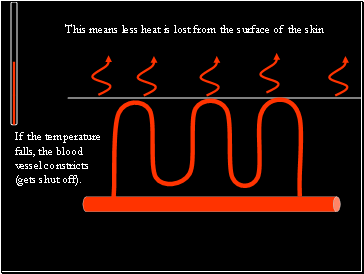
If the temperature falls, the blood vessel constricts (gets shut off).
This means less heat is lost from the surface of the skin
Slide 16
What mechanisms are there to warm the body up?
Piloerection
This is when the hairs on your skin “stand up” .
It is sometimes called “goose bumps” or “chicken skin”!
The hairs trap a layer of air next to the skin which is then warmed by the body heat
The air becomes an insulating layer.
Slide 17
Slide 18
Controlling Glucose levels
Your cells also need an exact level of glucose in the blood.
Excess glucose gets turned into glycogen in the liver
This is regulated by 2 hormones (chemicals) from the pancreas called:
Insulin
Glucagon
Slide 19
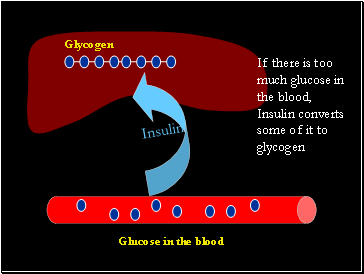
If there is too much glucose in the blood, Insulin converts some of it to glycogen
Glycogen
Insulin
Glucose in the blood
Slide 20
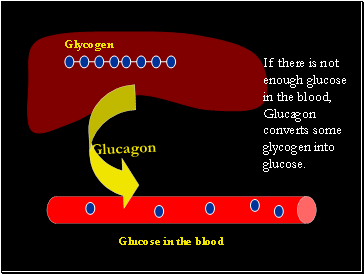
If there is not enough glucose in the blood, Glucagon converts some glycogen into glucose.
Glycogen
Glucagon
Glucose in the blood
Slide 21
Diabetes
Some people do not produce enough insulin.
When they eat food, the glucose levels in their blood cannot be reduced.
This condition is known as DIABETES.
Diabetics sometimes have to inject insulin into their blood. They have to be careful of their diet.
Contents
- Glossary
- What is Homeostasis?
- Controlling body temperature
- Penguins huddling to keep warm
- Sweating
- Controlling Glucose levels
- Diabetes
- Controlling water levels
- The kidneys
- Reabsorbing water
- Summary of urine production
Last added presentations
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Thermal Energy
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation