Absorption ProcessPage
1
1
Slide 1
Absorption Process
Intermediate 2 Biology
Slide 2
Learning Intentions
15th Jan
Everyone should complete:
1-Absorption Model
2-Visking Tube Experiment
3-Small Intestine
Most people will complete:
The Check Test for 9.6
The Home Practice for 9.6
Some people might start:
Problem solving
Torrance Intermediate 2 Biology textbook
p 240 ‘Applying Your Knowledge’
Slide 3
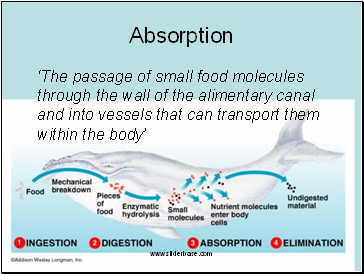
Absorption
The alimentary canal (or gut) is a long tube inside the body
Any food in the alimentary canal is still outside the cells of the body
To get inside the molecules of the food have to be able to pass through the wall of the alimentary canal
Now try the ‘Model Absorption’ kit!
Slide 4
Think…
What does the piece of tube in the model represent?
Why can the food molecules inside the tube still be regarded as ‘outside’ the body?
Which food molecules in the model were able to pass through the wall of the tube most easily? Why was this?
Why were the protein molecules in the model unable to pass through the wall of the tube?
Now complete the ‘Notes’!!!
Slide 5
Absorption
‘The passage of small food molecules through the wall of the alimentary canal and into vessels that can transport them within the body’
Slide 6
Visking Tubing Experiment
a diagram of the experiment when set up
what the visking tubing was being used to represent
how you tested for starch and glucose and a table of your results
an explanation of the results in terms of size of the food molecules involved
Slide 7
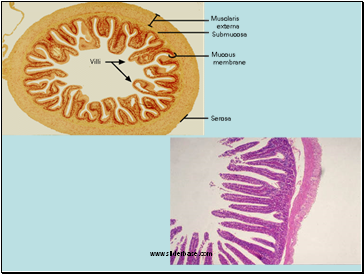
Small Intestine
Small, soluble food molecules are absorbed through the wall of the small intestine
To absorb food molecules efficiently the small intestine has three main adaptations…….
Slide 8
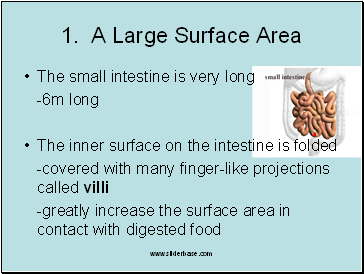
A Large Surface Area
The small intestine is very long
-6m long
The inner surface on the intestine is folded
-covered with many finger-like projections called villi
-greatly increase the surface area in contact with digested food
Slide 9
Slide 10
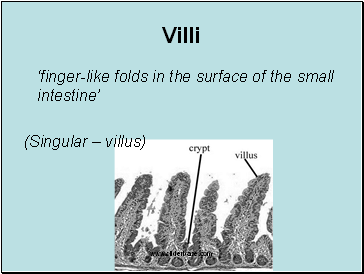
Villi
1 2
Contents
- Absorption Process
- Learning Intentions
- Absorption
- Visking Tubing Experiment
- Small Intestine
- A Large Surface Area
- Villi
- Good Blood Supply
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Mechanics Lecture
- Health Physics
- Buoyancy
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Space Radiation