MakingFoodPage
5
5
DEFINITION
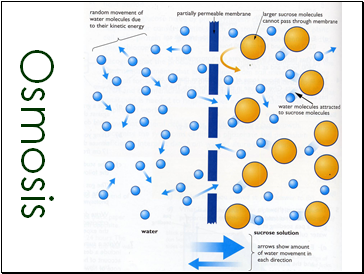
Osmosis is the net diffusion of water across a partially permeable membrane, from a solution with a high water concentration (HWC) to one with a low water concentration (LWC).
Slide 34
Osmosis
Slide 35
Osmosis
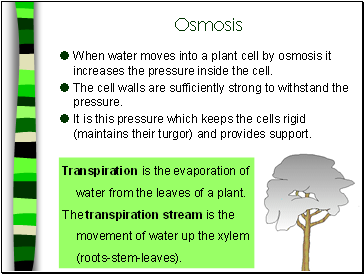
When water moves into a plant cell by osmosis it increases the pressure inside the cell.
The cell walls are sufficiently strong to withstand the pressure.
It is this pressure which keeps the cells rigid (maintains their turgor) and provides support.
Transpiration is the evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant.
The transpiration stream is the movement of water up the xylem (roots-stem-leaves).
Slide 36
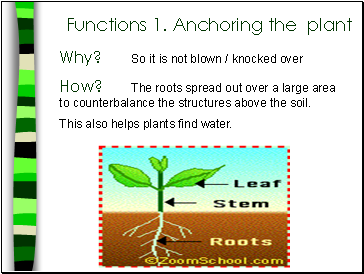
Why? So it is not blown / knocked over
How? The roots spread out over a large area to counterbalance the structures above the soil.
This also helps plants find water.
Functions 1. Anchoring the plant
Slide 37
2. Absorb essential nutrients
Why? To take up substances to survive.
How? Roots have tiny hairs on their surface which increases their surface area to maximise absorption.
Slide 38
3. Absorb water
Why? Water is a raw material for photosynthesis.
How? Root hairs increase surface area.
Slide 39
Transport in Flowering Plants
In flowering plants there are separate transport systems for water and nutrients.
Substances are transported in vascular bundles made up of the xylem and the phloem.
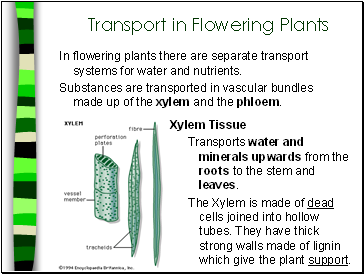
Xylem Tissue
Transports water and minerals upwards from the roots to the stem and leaves.
The Xylem is made of dead cells joined into hollow tubes. They have thick strong walls made of lignin which give the plant support.
Slide 40
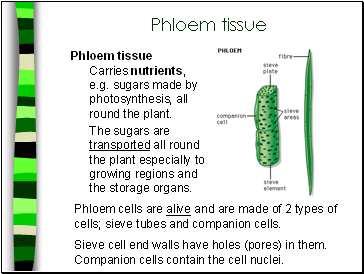
Phloem tissue
Phloem tissue
Carries nutrients,
e.g. sugars made by photosynthesis, all round the plant.
The sugars are transported all round the plant especially to growing regions and the storage organs.
Phloem cells are alive and are made of 2 types of cells; sieve tubes and companion cells.
Sieve cell end walls have holes (pores) in them. Companion cells contain the cell nuclei.
Slide 41
Sugar cane
Vascular bundles are composed of Xylem, Phloem and Fibres which support and protect the xylem and phloem.
Leaf Veins are Vascular Bundles.
Contents
- The World of Plants
- Plants- the first link
- Plant survival
- Mans’ uses of plant glucose
- Glucose molecule
- Gas Balance
- Summary of Photosynthesis
- Internal structure
- Outer layer- upper surface
- Outer layer- bottom surface
- Stomata- open
- Stomata- closed
- General structure
- Leaf veins
- Roots
- Into the root hair cell
- Transport in Flowering Plants
- Phloem tissue
- Sugar cane
- Vascular bundles
- Xylem & phloem in stem
- Position of vascular tissue in the stem
- What Limits photosynthesis?
- Factors limiting photosynthesis
- Helping plants to grow
- Signs of Nutrient deficiency in plants
Last added presentations
- Upcoming Classes
- Buoyancy
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Newton's laws of motion
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Gravitation
- History of Modern Astronomy