Electron MicroscopePage
1
1
Slide 1
AS Biology Core Principles
The Electron Microscope
Slide 2
Aims
Resolving power
The resolving power of light & electron microscopes
The difference between the light & electron microscope
Transmission & scanning electron microscopy
Slide 3
Introduction
Microscopes magnify & resolve images
Microscopy began in 1665 when Robert Hooke coined the word ‘cells’ to describe the structure of cork
You need to know about 2 types of microscope - light & electron
You need to know how they work and the differences between them
‘Its not how much they magnify that is key - but how well they resolve…’
Slide 4
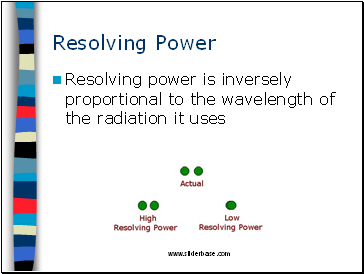
Resolving Power
The limit of resolution of a microscope is the smallest distance between 2 points that can be seen using a microscope
This is a measure of the clarity of the image
A microscope with a high resolving power will allow 2 small objects which are close together to be seen as 2 distinct objects
Slide 5
Resolving Power
Resolving power is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the radiation it uses
Slide 6
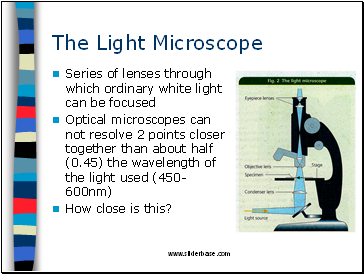
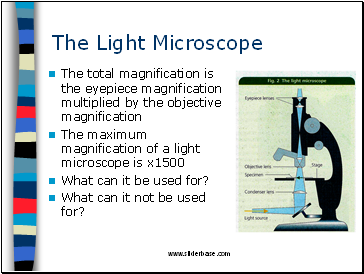
The Light Microscope
Series of lenses through which ordinary white light can be focused
Optical microscopes can not resolve 2 points closer together than about half (0.45) the wavelength of the light used (450-600nm)
How close is this?
Slide 7
The Light Microscope
The total magnification is the eyepiece magnification multiplied by the objective magnification
The maximum magnification of a light microscope is x1500
What can it be used for?
What can it not be used for?
Slide 8
The Electron Microscope
Electrons (negatively charged, very small particles) can behave as waves
The wavelength of electrons is about 0.005nm
What will this mean for the limit of resolution?
Electrons are ‘fired’ from an electron gun at the specimen and onto a fluorescent screen or photographic plate
Where is this technique commonly used?
There are 2 types of electron microscopy - transmission and scanning
Both focus an electron beam onto the specimen using electromagnets
Slide 9
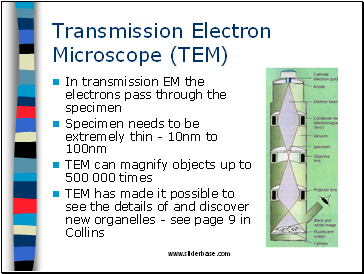
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
1 2
Contents
- The Electron Microscope
- Aims
- Introduction
- Resolving Power
- Resolving Power
- The Light Microscope
- The Electron Microscope
- Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Links
- Light & Electron Microscopes
Last added presentations
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Gravitation
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Radiation
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Sound