Bonding, Molecular Shape & StructurePage
5
5
Non-symmetrical molecules (e.g. CHCl3, CO(CH3)2, H2O) are Polar.
The dipoles are not all equal or in opposite directions (partial charges and bond lengths are all different in C-Cl, C-H, C=O, C-H)
(H2O is a bent molecule not linear, see later notes)
Slide 29
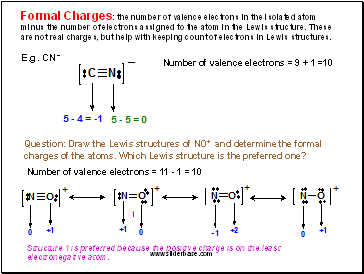
Formal Charges: the number of valence electrons in the isolated atom minus the number of electrons assigned to the atom in the Lewis structure. These are not real charges, but help with keeping count of electrons in Lewis structures.
E.g. CN-
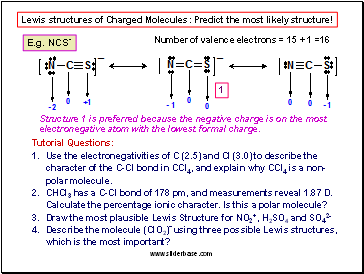
Question: Draw the Lewis structures of NO+ and determine the formal charges of the atoms. Which Lewis structure is the preferred one?
Number of valence electrons = 9 + 1 =10
Number of valence electrons = 11 - 1 = 10
Structure 1 is preferred because the positive charge is on the least electronegative atom.
1
Slide 30
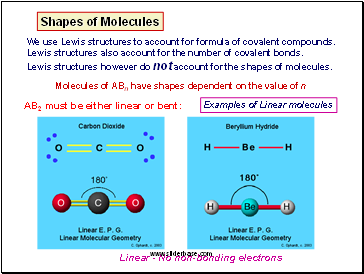
Lewis structures of Charged Molecules: Predict the most likely structure!
E.g. NCS-
Number of valence electrons = 15 + 1 =16
Structure 1 is preferred because the negative charge is on the most electronegative atom with the lowest formal charge.
1
Tutorial Questions:
Use the electronegativities of C (2.5) and Cl (3.0) to describe the character of the C-Cl bond in CCl4, and explain why CCl4 is a non-polar molecule.
CHCl3 has a C-Cl bond of 178 pm, and measurements reveal 1.87 D. Calculate the percentage ionic character. Is this a polar molecule?
Draw the most plausible Lewis Structure for NO2+, H2SO4 and SO42-
Describe the molecule (ClO2)- using three possible Lewis structures, which is the most important?
Slide 31
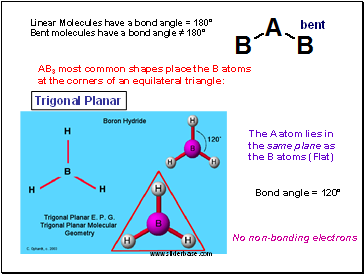
Shapes of Molecules
We use Lewis structures to account for formula of covalent compounds.
Lewis structures also account for the number of covalent bonds.
Lewis structures however do not account for the shapes of molecules.
Molecules of ABn have shapes dependent on the value of n
AB2 must be either linear or bent:
Examples of Linear molecules
Linear - No non-bonding electrons
Slide 32
Linear Molecules have a bond angle = 180°
Bent molecules have a bond angle ≠ 180°
AB3 most common shapes place the B atoms at the corners of an equilateral triangle:
bent
Trigonal Planar
The A atom lies in the same plane as the B atoms (Flat)
Bond angle = 120°
No non-bonding electrons
Slide 33
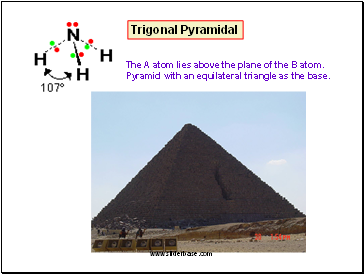
Trigonal Pyramidal
The A atom lies above the plane of the B atom.
Pyramid with an equilateral triangle as the base.
Slide 34
Contents
- Lewis Symbols
- Pauling scale of electronegativity;
- Electronegativity is dictated by
- Shapes of Molecules
- Trigonal Pyramidal
- Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
- Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
- Molecules with Expanded Valence Shells
- Hydrogen Bonding & Water
- Dipole-dipole Attractive Forces
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Motion
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions