The ATOMPage
3
3
stability is a function of having a full complement of valence electrons.
Atoms that do not have full electrons energy levels are unstable and must gain, lose or share electrons to become stable.
other atoms can become more stable by reacting and changing the number of their electrons
Slide 24
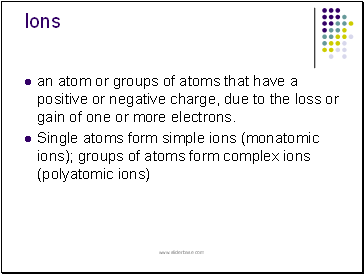
Stable Atoms
atoms can follow one of 2 rules:
a) Octet rule - atoms attempt to obtain 8 valence electrons
- includes most atoms
b) Duet rule - atoms attempt to obtain 2 valence electrons
- includes H, Li and Be
Atoms can achieve a stable octet or duet by forming ions.
Slide 25
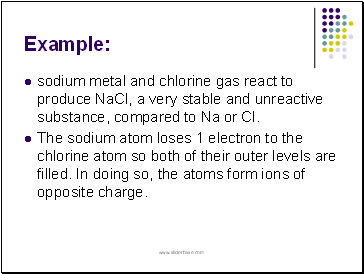
Ions
an atom or groups of atoms that have a positive or negative charge, due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
Single atoms form simple ions (monatomic ions); groups of atoms form complex ions (polyatomic ions)
Slide 26
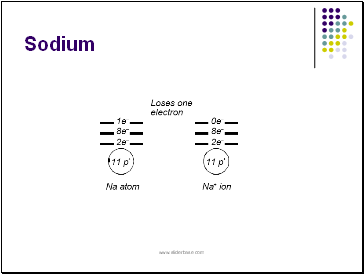
Example:
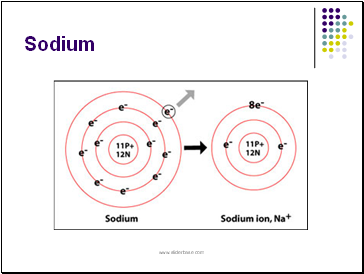
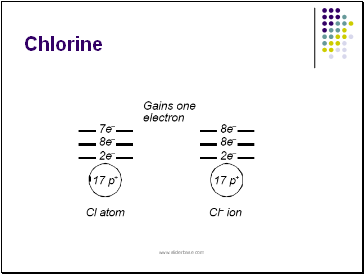
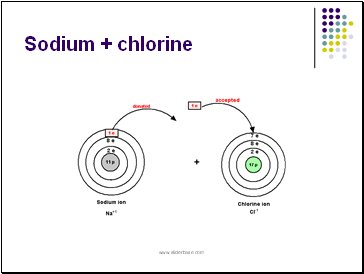
sodium metal and chlorine gas react to produce NaCl, a very stable and unreactive substance, compared to Na or Cl.
The sodium atom loses 1 electron to the chlorine atom so both of their outer levels are filled. In doing so, the atoms form ions of opposite charge.
Slide 27
Sodium
Slide 28
Sodium
Slide 29
Chlorine
Slide 30
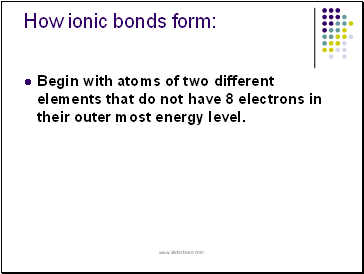
How ionic bonds form:
Begin with atoms of two different elements that do not have 8 electrons in their outer most energy level.
Slide 31
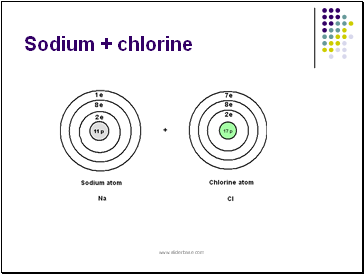
Sodium + chlorine
Slide 32
The sodium atom (Na ) donates 1 electron becoming a positively sodium ion ( Na+).
The chlorine atom (Cl) accepts the donated electron becoming a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-).
Slide 33
Sodium + chlorine
Contents
- Atoms
- Models of the Atom - History
- John Dalton (1803)
- J. J. Thomson (1897)
- Ernest Rutherford (1908) - Nuclear
- Neils Bohr (1913)
- Quantum Mechanics Model
- Drawing Bohr Diagrams
- Stable Atoms
- Ions
- Sodium
- Chlorine
- How ionic bonds form:
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Newton's Laws
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Friction
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Madame Marie Curie