History of Long-Range Photography in AstronomyPage
5
5
Slide 28
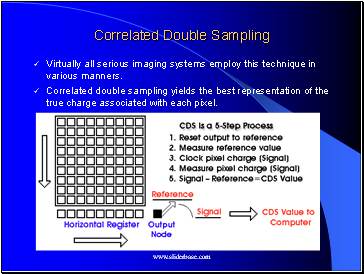
Correlated Double Sampling
Virtually all serious imaging systems employ this technique in various manners.
Correlated double sampling yields the best representation of the true charge associated with each pixel.
Slide 29
Other Factors
Weight
Electronics Modules
Surface mount technology
Stay away from cameras with bulky external control boxes
Number of camera connections
Camera start-up procedures
Peltier Cooler
Starlight Xpress – just plug in he camera
SBIG – Controlled by software
Cooling Fans
Can induce vibrations
Slide 30
Other Factors
Is the software user friendly
Drop-down menus
Dialog boxes
Keyboard shortcuts
Learning curve of the camera
Large instruction manuals
Using your camera should be an enjoyable experience
Slide 31
Basic Imaging Concepts
Slide 32
More “Buzz” Words
Bias Frames
Light Boxes
T-Shirt Flats
Flat Fields
Dark Frames
Raw Imagines
Calibrated Image
Signal vs. Noise
Slide 33
Bias Frames
Astronomers make bias frames to capture the bias level.
Bias frames represent noise levels that occur on a CCD detector when placed in total darkness with an integration time of zero.
These frames represent the minimum noise generated by the camera electronics as pixel values are read from the CCD array.
This bias level can fluctuate because of things that happen every time the CCD is read out or because extraneous signals are added to the bias level. These un-patterned events can originate in power supplies, nearby electronics, motors, and radio-frequency interference from computers and monitors.
The noise in these bias frames is extremely low; so many CCD imagers do not bother to apply them to their images.
Slide 34
Why take Bias Frames?
They give you a history of your cameras operational functionally.
Noise level changes
Interference
They are needed if you intend to do astrometry, photometry or to get the best results from your images.
NOTE: SBIG cameras add a 100-unit pedestal to each Bias, Dark, Flat-
Field, and Light frame. This pedestal value is subtracted by
CCDSoft during the data reduction process. This will need to be
subtracted manually with other IP programs.
Slide 35
Contents
- Optical Sensors used in Astronomy
- My Telescope “1979”
- Optical Sensors used in Astronomy
- CCD Camera “Buzz” Words
- Deep Sky Imaging
- Planetary Imaging
- CCD Array Sensor
- Sampling
- Pixel Sensitivity
- Pixel Binning
- Bloomimg vs. Anti-Blooming
- Readout Noise
- Thermal Noise
- System Gain
- Digitization
- Dynamic Range
- Charge Transfer Efficiency
- Data Rate and Transfer Rate
- Correlated Double Sampling
- Other Factors
- Basic Imaging Concepts
- Why take Bias Frames?
- Dark Frames
- Cosmic Rays
- Flat Fields
- Spatial Filtering
- Convolution Kernel
- Convolution Matrix
- Median Filter
- High-Pass
- Deconvolution
- Asteroid Data Screen
- Ephemeris Generator
- Calculated Measurement Screen
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Sound
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Friction
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation