History of Long-Range Photography in AstronomyPage
7
7
Slide 47
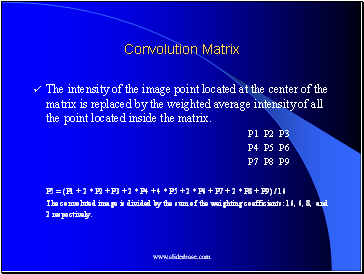
Convolution Matrix
The intensity of the image point located at the center of the matrix is replaced by the weighted average intensity of all the point located inside the matrix.
P1 P2 P3
P4 P5 P6
P7 P8 P9
P5 = (P1 + 2 * P2 + P3 + 2 * P4 + 4 * P5 + 2 * P6 + P7 + 2 * P8 + P9) / 16
The convoluted image is divided by the sum of the weighting coefficients: 16, 6, 8, and 2 respectively.
Slide 48
Median Filter
A variation on low-pass filtering and is better at eliminating noise.
Instead of replacing a pixel with the average of its neighbors, it is replaced with the median within the ensemble.
This filter is good for removing “hot” and “cold” pixels from an image.
Slide 49
High-Pass
A high-pass filter emphasizes fine detail in an image – exactly the opposite of what a low-pass filter does.
High-pass filters work exactly the same way, except that they use a different kernel.
High-pass filters can sharpen an image blurred by atmospheric seeing or poor focus.
Unfortunately, their effect on noise is also the opposite of a low-pass filter; noise becomes amplified.
Slide 50
Unsharp Masking
Unsharp masking is a variation of the high-pass filtering.
A low pass filter is first used to make a blurry copy of the original images.
This copy is subtracted from the original, suppressing large-scale features and leaving fine detail.
Unsharp masking is very effective for planetary imaging
Do not overdo high-pass filtering, since small, faint details can be greatly exaggerated. The result might not be a realistic view of the object.
An over processed image will look grainy and unnatural.
Slide 51
Deconvolution
Once we filter an image, we can undo the results through a process called deconvolution.
With deconvolution,instead of multiplying pixel data by a filter, we divide it.
Deconvolution can reduce the effects of atmospheric seeing and even defects created by poor optics.
Slide 52
Spatial Filtering Summary
Here are some guidelines I’ve found useful:
Low-pass filtering is good for picking faint nebulosity out of noisy images.
High-pass filtering and unsharp masking works well on lunar and planetary images.
Median filtering is good for reducing the noise in an image, particularly hot and cold pixels.
Deconvolution works well on high-resolution images.
After passing an image through a filtering algorith, try processing it with a stretching function.
Contents
- Optical Sensors used in Astronomy
- My Telescope “1979”
- Optical Sensors used in Astronomy
- CCD Camera “Buzz” Words
- Deep Sky Imaging
- Planetary Imaging
- CCD Array Sensor
- Sampling
- Pixel Sensitivity
- Pixel Binning
- Bloomimg vs. Anti-Blooming
- Readout Noise
- Thermal Noise
- System Gain
- Digitization
- Dynamic Range
- Charge Transfer Efficiency
- Data Rate and Transfer Rate
- Correlated Double Sampling
- Other Factors
- Basic Imaging Concepts
- Why take Bias Frames?
- Dark Frames
- Cosmic Rays
- Flat Fields
- Spatial Filtering
- Convolution Kernel
- Convolution Matrix
- Median Filter
- High-Pass
- Deconvolution
- Asteroid Data Screen
- Ephemeris Generator
- Calculated Measurement Screen
Last added presentations
- Gravitation
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Motion
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Sound
- Radiation
- Newton's laws of motion