The Milky Way GalaxyPage
7
7
positions interior to Sun’s orbit in Galaxy have some distance ambiguity
Less distance ambiguity outside of Solar orbit, and better evidence of arm-like morphology
Spiral Structure
Slide 35
The Galactic Nucleus
Inner 500pc of Galaxy
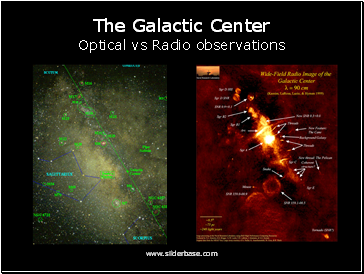
Extinction makes optical studies impossible - use radio or IR
Observe ionized gas, line emission, dust, star clusters
Stellar density is 107 stars per pc3 (compared to 0.1 in the solar neighborhood)
If the Sun were near the GC
Nearest star would be 1000AU away
A million stars brighter than Sirius in the night sky
Total starlight more than 200 times brightness of the full Moon
Slide 36
The Galactic Center
Optical vs Radio observationsSlide 37
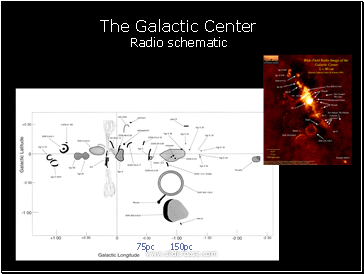
75pc 150pc
The Galactic Center Radio schematic
Slide 38
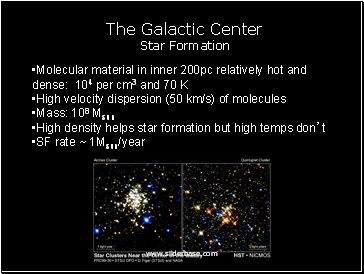
Molecular material in inner 200pc relatively hot and dense: 104 per cm3 and 70 K
High velocity dispersion (50 km/s) of molecules
Mass: 108 Msun
High density helps star formation but high temps don’t
SF rate ~ 1Msun/year
The Galactic Center Star Formation
Slide 39
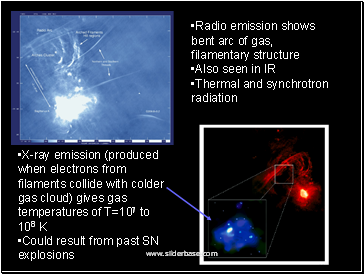
Radio emission shows bent arc of gas, filamentary structure
Also seen in IR
Thermal and synchrotron radiation
X-ray emission (produced when electrons from filaments collide with colder gas cloud) gives gas temperatures of T=107 to 108 K
Could result from past SN explosions
Slide 40
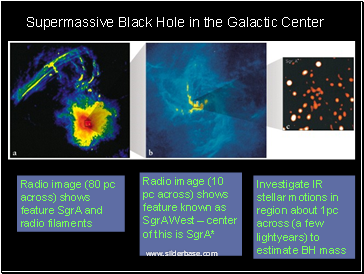
Supermassive Black Hole in the Galactic Center
Radio image (80 pc across) shows feature SgrA and radio filaments
Radio image (10 pc across) shows feature known as SgrA West – center of this is SgrA*
Investigate IR stellar motions in region about 1pc across (a few lightyears) to estimate BH mass
Slide 41
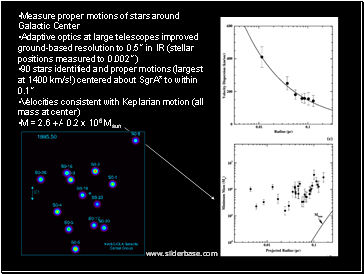
Measure proper motions of stars around Galactic Center
Adaptive optics at large telescopes improved ground-based resolution to 0.5” in IR (stellar positions measured to 0.002”)
90 stars identified and proper motions (largest at 1400 km/s!) centered about SgrA* to within 0.1”
Velocities consistent with Keplarian motion (all mass at center)
M = 2.6 +/- 0.2 x 106 Msun
Slide 42
Curvature of the paths near SgrA* constrain the volume of the mass to ~ Schwarzchild radius (few x 106 km) Supermassive Black Hole
Contents
- Differential Rotation
- Local Standard of Rest
- Position and Velocity of the LSR in Galaxy
- Measuring the Rotation Curve of the Milky Way
- What is the Dark Matter?
- Slight Aside on Determining Distances
- Spiral Structure
- The Galactic Nucleus
- The Galactic Center
Last added presentations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Sound
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Upcoming Classes