Osmoregulation and ExcretionPage
4
4
The kinds of nitrogenous wastes excreted depend on an animalís evolutionary history and habitat.
The amount of nitrogenous waste is coupled to the animalís energy budget.
Slide 23
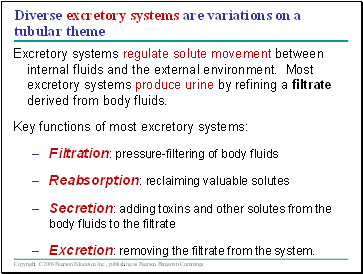
Diverse excretory systems are variations on a tubular theme
Excretory systems regulate solute movement between internal fluids and the external environment. Most excretory systems produce urine by refining a filtrate derived from body fluids.
Key functions of most excretory systems:
Filtration: pressure-filtering of body fluids
Reabsorption: reclaiming valuable solutes
Secretion: adding toxins and other solutes from the body fluids to the filtrate
Excretion: removing the filtrate from the system.
Slide 24
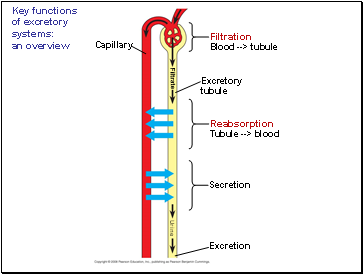
Key functions of excretory systems: an overview
Capillary
Excretion
Secretion
Reabsorption
Tubule --> blood
Excretory
tubule
Filtration
Blood --> tubule
Filtrate
Urine
Slide 25
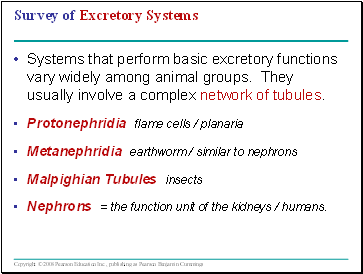
Survey of Excretory Systems
Systems that perform basic excretory functions vary widely among animal groups. They usually involve a complex network of tubules.
Protonephridia flame cells / planaria
Metanephridia earthworm / similar to nephrons
Malpighian Tubules insects
Nephrons = the function unit of the kidneys / humans.
Slide 26
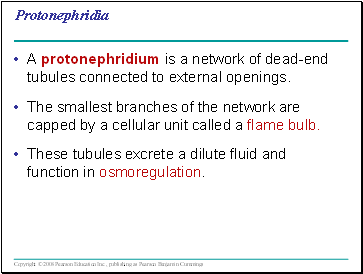
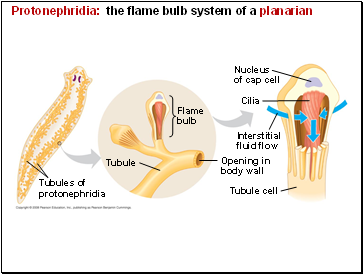
Protonephridia
A protonephridium is a network of dead-end tubules connected to external openings.
The smallest branches of the network are capped by a cellular unit called a flame bulb.
These tubules excrete a dilute fluid and function in osmoregulation.
Slide 27
Protonephridia: the flame bulb system of a planarian
Tubule
Tubules of
protonephridia
Cilia
Interstitial
fluid flow
Opening in
body wall
Nucleus
of cap cell
Flame
bulb
Tubule cell
Slide 28
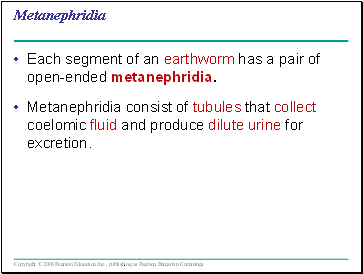
Metanephridia
Each segment of an earthworm has a pair of open-ended metanephridia.
Metanephridia consist of tubules that collect coelomic fluid and produce dilute urine for excretion.
Slide 29
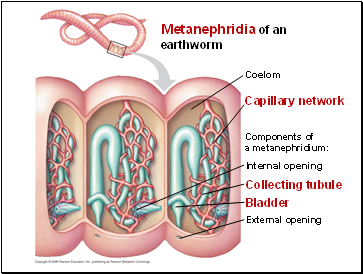
Metanephridia of an earthworm
Capillary network
Components of
a metanephridium:
External opening
Coelom
Collecting tubule
Internal opening
Bladder
Slide 30
Malpighian Tubules
Contents
- A Balancing Act
- Osmoregulation balances the uptake and loss of water and solutes
- Osmotic Challenges
- Marine Animals
- Freshwater Animals
- Animals That Live in Temporary Waters
- Land Animals
- Energetics of Osmoregulation
- An animalís nitrogenous wastes reflect its phylogeny and habitat
- Animals Excrete Different Forms of Nitrogenous Wastes
- Diverse excretory systems are variations on a tubular theme
- Survey of Excretory Systems
- Protonephridia
- Metanephridia
- Malpighian Tubules
- Pathway of the Filtrate
- Blood Vessels Associated with the Nephrons
- The nephron is organized for stepwise processing of blood filtrate
- Solute Gradients and Water Conservation
- Adaptations of the Vertebrate Kidney to Diverse Environments
- Hormonal circuits link kidney function, water balance, and blood pressure
- The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
- Homeostatic Regulation of the Kidney
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Gravitation
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Newton's Laws
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants