PhotosynthesisPage
8
8
Slide 64
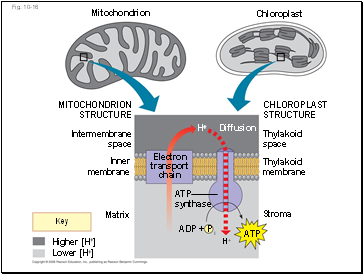
In mitochondria, protons are pumped to the intermembrane space and drive ATP synthesis as they diffuse back into the mitochondrial matrix
In chloroplasts, protons are pumped into the thylakoid space and drive ATP synthesis as they diffuse back into the stroma
Slide 65
Fig. 10-16
Key
Mitochondrion
Chloroplast
CHLOROPLAST
STRUCTURE
MITOCHONDRION
STRUCTURE
Intermembrane
space
Inner
membrane
Electron
transport
chain
H+
Diffusion
Matrix
Higher [H+]
Lower [H+]
Stroma
ATP
synthase
ADP + P
i
H+
ATP
Thylakoid
space
Thylakoid
membrane
Slide 66
ATP and NADPH are produced on the side facing the stroma, where the Calvin cycle takes place
In summary, light reactions generate ATP and increase the potential energy of electrons by moving them from H2O to NADPH
Slide 67
Fig. 10-17
Light
Fd
Cytochrome
complex
ADP
+
i
H+
ATP
P
ATP
synthase
To
Calvin
Cycle
STROMA
(low H+ concentration)
Thylakoid
membrane
THYLAKOID SPACE
(high H+ concentration)
STROMA
(low H+ concentration)
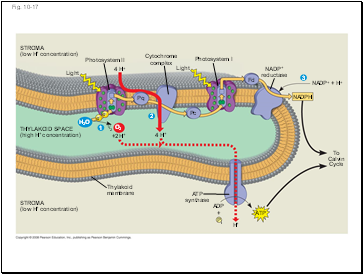
Photosystem II
Photosystem I
4 H+
4 H+
Pq
Pc
Light
NADP+
reductase
NADP+ + H+
NADPH
+2 H+
H2O
O2
e–
e–
1/2
1
2
3
Slide 68
Concept 10.3: The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar
The Calvin cycle, like the citric acid cycle, regenerates its starting material after molecules enter and leave the cycle
The cycle builds sugar from smaller molecules by using ATP and the reducing power of electrons carried by NADPH
Slide 69
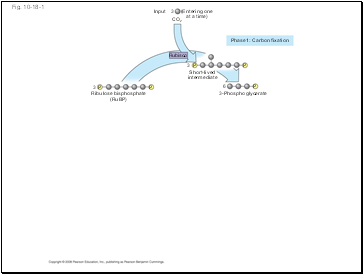
Carbon enters the cycle as CO2 and leaves as a sugar named glyceraldehyde-3-phospate (G3P)
For net synthesis of 1 G3P, the cycle must take place three times, fixing 3 molecules of CO2
The Calvin cycle has three phases:
Carbon fixation (catalyzed by rubisco)
Reduction
Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor (RuBP)
Slide 70
Fig. 10-18-1
Ribulose bisphosphate
(RuBP)
3-Phosphoglycerate
Short-lived
intermediate
Phase 1: Carbon fixation
(Entering one
at a time)
Rubisco
Input
CO2
P
3
6
3
3
P
P
P
P
Slide 71
Contents
- The Process That Feeds the Biosphere
- Chloroplasts: The Sites of Photosynthesis in Plants
- The Splitting of Water
- Photosynthesis as a Redox Process
- The Two Stages of Photosynthesis: A Preview
- The Nature of Sunlight
- Photosynthetic Pigments: The Light Receptors
- Excitation of Chlorophyll by Light
- A Photosystem: A Reaction-Center Complex Associated with Light-Harvesting Complexes
- Linear Electron Flow
- Cyclic Electron Flow
- A Comparison of Chemiosmosis in Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
- Photorespiration: An Evolutionary Relic?
- C4 Plants
- CAM Plants
- The Importance of Photosynthesis: A Review
Last added presentations
- Motion
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Solar Energy
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Sound
- Newton’s third law of motion