Regulation of Gene ExpressionPage
5
5
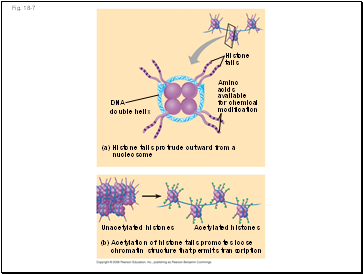
This process loosens chromatin structure, thereby promoting the initiation of transcription
The addition of methyl groups (methylation) can condense chromatin; the addition of phosphate groups (phosphorylation) next to a methylated amino acid can loosen chromatin
Animation: DNA Packing
Slide 29
Fig. 18-7
Histone
tails
DNA
double helix
(a) Histone tails protrude outward from a
nucleosome
Acetylated histones
Amino
acids
available
for chemical
modification
(b) Acetylation of histone tails promotes loose
chromatin structure that permits transcription
Unacetylated histones
Slide 30
The histone code hypothesis proposes that specific combinations of modifications help determine chromatin configuration and influence transcription
Slide 31
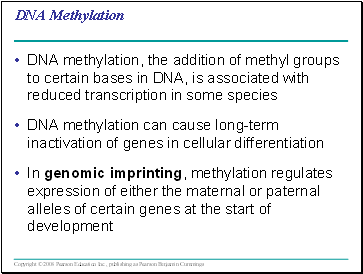
DNA Methylation
DNA methylation, the addition of methyl groups to certain bases in DNA, is associated with reduced transcription in some species
DNA methylation can cause long-term inactivation of genes in cellular differentiation
In genomic imprinting, methylation regulates expression of either the maternal or paternal alleles of certain genes at the start of development
Slide 32
Epigenetic Inheritance
Although the chromatin modifications just discussed do not alter DNA sequence, they may be passed to future generations of cells
The inheritance of traits transmitted by mechanisms not directly involving the nucleotide sequence is called epigenetic inheritance
Slide 33
Regulation of Transcription Initiation
Chromatin-modifying enzymes provide initial control of gene expression by making a region of DNA either more or less able to bind the transcription machinery
Slide 34
Organization of a Typical Eukaryotic Gene
Associated with most eukaryotic genes are control elements, segments of noncoding DNA that help regulate transcription by binding certain proteins
Control elements and the proteins they bind are critical to the precise regulation of gene expression in different cell types
Slide 35
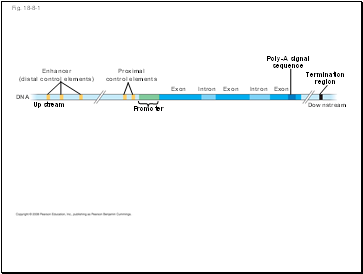
Fig. 18-8-1
Enhancer
(distal control elements)
Proximal
control elements
Poly-A signal
sequence
Termination
region
Downstream
Promoter
Upstream
DNA
Exon
Exon
Exon
Intron
Intron
Slide 36
Contents
- Conducting the Genetic Orchestra
- Operons: The Basic Concept
- Repressible and Inducible Operons: Two Types of Negative Gene Regulation
- Positive Gene Regulation
- Differential Gene Expression
- Regulation of Chromatin Structure
- Regulation of Transcription Initiation
- Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation
- Effects on mRNAs by MicroRNAs and Small Interfering RNAs
- Chromatin Remodeling and Silencing of Transcription by Small RNAs
- A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
- Cytoplasmic Determinants and Inductive Signals
- Sequential Regulation of Gene Expression During Cellular Differentiation
- Pattern Formation: Setting Up the Body Plan
- Types of Genes Associated with Cancer
- Interference with Normal Cell-Signaling Pathways
- The Multistep Model of Cancer Development
- Inherited Predisposition and Other Factors Contributing to Cancer
Last added presentations
- Waves & Sound
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Upcoming Classes
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Madame Marie Curie
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal