Regulation of Gene ExpressionPage
7
7
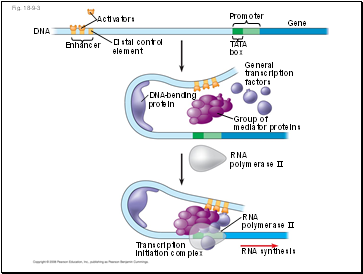
Fig. 18-9-3
Enhancer
TATA
box
Promoter
Activators
DNA
Gene
Distal control
element
Group of
mediator proteins
DNA-bending
protein
General
transcription
factors
RNA
polymerase II
RNA
polymerase II
Transcription
initiation complex
RNA synthesis
Slide 44
Some transcription factors function as repressors, inhibiting expression of a particular gene
Some activators and repressors act indirectly by influencing chromatin structure to promote or silence transcription
Slide 45
A particular combination of control elements can activate transcription only when the appropriate activator proteins are present
Combinatorial Control of Gene Activation
Slide 46
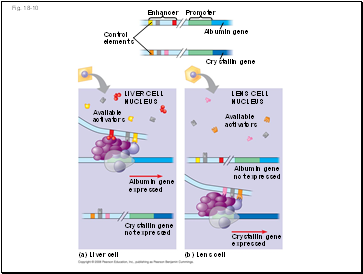
Fig. 18-10
Control
elements
Enhancer
Available
activators
Albumin gene
(b) Lens cell
Crystallin gene
expressed
Available
activators
LENS CELL
NUCLEUS
LIVER CELL
NUCLEUS
Crystallin gene
Promoter
(a) Liver cell
Crystallin gene
not expressed
Albumin gene
expressed
Albumin gene
not expressed
Slide 47
Coordinately Controlled Genes in Eukaryotes
Unlike the genes of a prokaryotic operon, each of the coordinately controlled eukaryotic genes has a promoter and control elements
These genes can be scattered over different chromosomes, but each has the same combination of control elements
Copies of the activators recognize specific control elements and promote simultaneous transcription of the genes
Slide 48
Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation
Transcription alone does not account for gene expression
Regulatory mechanisms can operate at various stages after transcription
Such mechanisms allow a cell to fine-tune gene expression rapidly in response to environmental changes
Slide 49
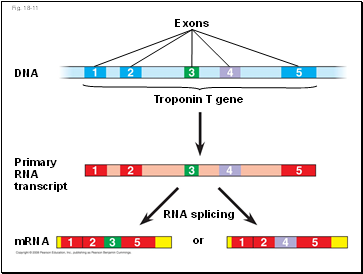
RNA Processing
In alternative RNA splicing, different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and which as introns
Animation: RNA Processing
Slide 50
Fig. 18-11
or
RNA splicing
mRNA
Primary
RNA
transcript
Troponin T gene
Exons
DNA
Slide 51
Contents
- Conducting the Genetic Orchestra
- Operons: The Basic Concept
- Repressible and Inducible Operons: Two Types of Negative Gene Regulation
- Positive Gene Regulation
- Differential Gene Expression
- Regulation of Chromatin Structure
- Regulation of Transcription Initiation
- Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation
- Effects on mRNAs by MicroRNAs and Small Interfering RNAs
- Chromatin Remodeling and Silencing of Transcription by Small RNAs
- A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
- Cytoplasmic Determinants and Inductive Signals
- Sequential Regulation of Gene Expression During Cellular Differentiation
- Pattern Formation: Setting Up the Body Plan
- Types of Genes Associated with Cancer
- Interference with Normal Cell-Signaling Pathways
- The Multistep Model of Cancer Development
- Inherited Predisposition and Other Factors Contributing to Cancer
Last added presentations
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Radiation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Newton's Laws
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Waves & Sound