Regulation of Gene ExpressionPage
4
4
transcribes
Inactive lac
repressor
lacZ
Operator
Promoter
DNA
CAP-binding site
lacI
RNA
polymerase less
likely to bind
Inactive
CAP
(a) Lactose present, glucose scarce (cAMP level
high): abundant lac mRNA synthesized
Slide 22
Concept 18.2: Eukaryotic gene expression can be regulated at any stage
All organisms must regulate which genes are expressed at any given time
In multicellular organisms gene expression is essential for cell specialization
Slide 23
Differential Gene Expression
Almost all the cells in an organism are genetically identical
Differences between cell types result from differential gene expression, the expression of different genes by cells with the same genome
Errors in gene expression can lead to diseases including cancer
Gene expression is regulated at many stages
Slide 24
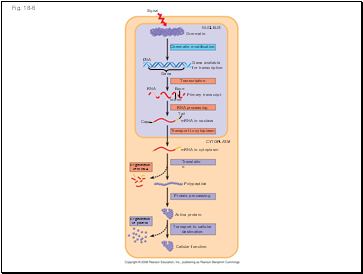
Fig. 18-6
DNA
Signal
Gene
NUCLEUS
Chromatin modification
Chromatin
Gene available
for transcription
Exon
Intron
Tail
RNA
Cap
RNA processing
Primary transcript
mRNA in nucleus
Transport to cytoplasm
mRNA in cytoplasm
Translation
CYTOPLASM
Degradation
of mRNA
Protein processing
Polypeptide
Active protein
Cellular function
Transport to cellular
destination
Degradation
of protein
Transcription
Slide 25
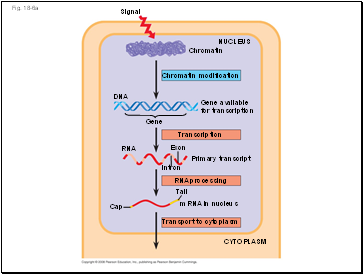
Fig. 18-6a
DNA
Signal
Gene
NUCLEUS
Chromatin modification
Chromatin
Gene available
for transcription
Exon
Intron
Tail
RNA
Cap
RNA processing
Primary transcript
mRNA in nucleus
Transport to cytoplasm
CYTOPLASM
Transcription
Slide 26
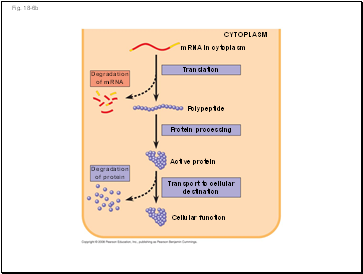
Fig. 18-6b
mRNA in cytoplasm
Translation
CYTOPLASM
Degradation
of mRNA
Protein processing
Polypeptide
Active protein
Cellular function
Transport to cellular
destination
Degradation
of protein
Slide 27
Regulation of Chromatin Structure
Genes within highly packed heterochromatin are usually not expressed
Chemical modifications to histones and DNA of chromatin influence both chromatin structure and gene expression
Slide 28
Histone Modifications
In histone acetylation, acetyl groups are attached to positively charged lysines in histone tails
Contents
- Conducting the Genetic Orchestra
- Operons: The Basic Concept
- Repressible and Inducible Operons: Two Types of Negative Gene Regulation
- Positive Gene Regulation
- Differential Gene Expression
- Regulation of Chromatin Structure
- Regulation of Transcription Initiation
- Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation
- Effects on mRNAs by MicroRNAs and Small Interfering RNAs
- Chromatin Remodeling and Silencing of Transcription by Small RNAs
- A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
- Cytoplasmic Determinants and Inductive Signals
- Sequential Regulation of Gene Expression During Cellular Differentiation
- Pattern Formation: Setting Up the Body Plan
- Types of Genes Associated with Cancer
- Interference with Normal Cell-Signaling Pathways
- The Multistep Model of Cancer Development
- Inherited Predisposition and Other Factors Contributing to Cancer
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Newton’s laws of motion
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Waves & Sound
- Solar Energy