Regulation of Gene ExpressionPage
1
1
Slide 1
Conducting the Genetic Orchestra
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences in cell types
RNA molecules play many roles in regulating gene expression in eukaryotes
Slide 2
Fig. 18-1
Slide 3
Concept 18.1: Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription
Natural selection has favored bacteria that produce only the products needed by that cell
A cell can regulate the production of enzymes by feedback inhibition or by gene regulation
Gene expression in bacteria is controlled by the operon model
Slide 4
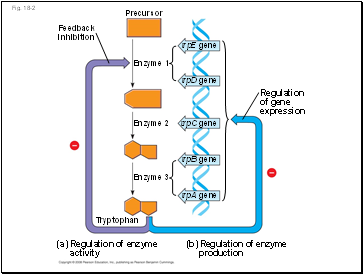
Fig. 18-2
Regulation
of gene
expression
trpE gene
trpD gene
trpC gene
trpB gene
trpA gene
(b) Regulation of enzyme
production
(a) Regulation of enzyme
activity
Enzyme 1
Enzyme 2
Enzyme 3
Tryptophan
Precursor
Feedback
inhibition
Slide 5
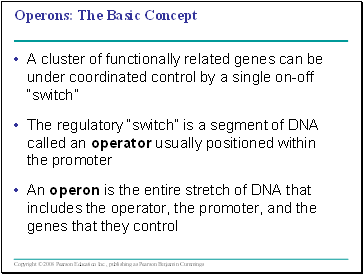
Operons: The Basic Concept
A cluster of functionally related genes can be under coordinated control by a single on-off “switch”
The regulatory “switch” is a segment of DNA called an operator usually positioned within the promoter
An operon is the entire stretch of DNA that includes the operator, the promoter, and the genes that they control
Slide 6
The operon can be switched off by a protein repressor
The repressor prevents gene transcription by binding to the operator and blocking RNA polymerase
The repressor is the product of a separate regulatory gene
Slide 7
The repressor can be in an active or inactive form, depending on the presence of other molecules
A corepressor is a molecule that cooperates with a repressor protein to switch an operon off
For example, E. coli can synthesize the amino acid tryptophan
Slide 8
By default the trp operon is on and the genes for tryptophan synthesis are transcribed
When tryptophan is present, it binds to the trp repressor protein, which turns the operon off
The repressor is active only in the presence of its corepressor tryptophan; thus the trp operon is turned off (repressed) if tryptophan levels are high
Contents
- Conducting the Genetic Orchestra
- Operons: The Basic Concept
- Repressible and Inducible Operons: Two Types of Negative Gene Regulation
- Positive Gene Regulation
- Differential Gene Expression
- Regulation of Chromatin Structure
- Regulation of Transcription Initiation
- Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation
- Effects on mRNAs by MicroRNAs and Small Interfering RNAs
- Chromatin Remodeling and Silencing of Transcription by Small RNAs
- A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
- Cytoplasmic Determinants and Inductive Signals
- Sequential Regulation of Gene Expression During Cellular Differentiation
- Pattern Formation: Setting Up the Body Plan
- Types of Genes Associated with Cancer
- Interference with Normal Cell-Signaling Pathways
- The Multistep Model of Cancer Development
- Inherited Predisposition and Other Factors Contributing to Cancer
Last added presentations
- Space Radiation
- Mechanics Lecture
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Solar Energy
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Waves & Sound