Bulk Properties of WaterPage
2
2
The energy required to change the temperature of the ice is the specific heat of ice
Slide 13
Energy and Phase Change
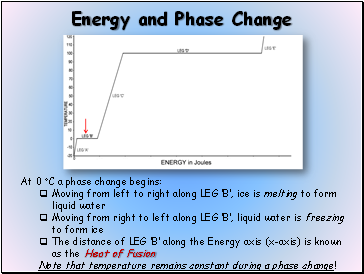
At 0 C a phase change begins:
Moving from left to right along LEG B, ice is melting to form liquid water
Moving from right to left along LEG B, liquid water is freezing to form ice
The distance of LEG B along the Energy axis (x-axis) is known as the Heat of Fusion
Note that temperature remains constant during a phase change!
Slide 14
Heat of Fusion
The energy that must be absorbed in order to convert solid to liquid at its melting point
The energy that must be removed in order to convert liquid to solid at its freezing point.
The heat of fusion of water is 334 Joules/gram
Slide 15
Energy and Phase Change
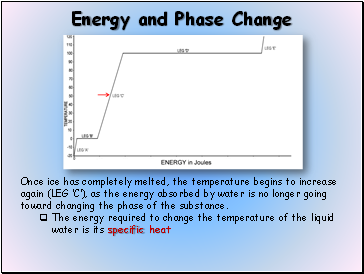
Once ice has completely melted, the temperature begins to increase again (LEG C), as the energy absorbed by water is no longer going toward changing the phase of the substance.
The energy required to change the temperature of the liquid water is its specific heat
Slide 16
Energy and Phase Change
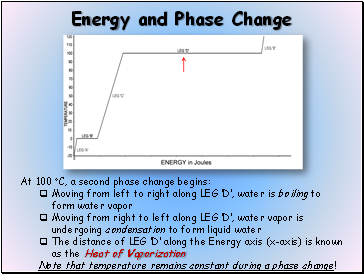
At 100 C, a second phase change begins:
Moving from left to right along LEG D, water is boiling to form water vapor
Moving from right to left along LEG D, water vapor is undergoing condensation to form liquid water
The distance of LEG D along the Energy axis (x-axis) is known as the Heat of Vaporization
Note that temperature remains constant during a phase change!
Slide 17
Heat of Vaporization
The energy that must be absorbed in order to convert a liquid to gas at its boiling point.
The energy that must be removed in order to convert a gas to liquid at its condensation point.
The heat of vaporization of water is 2260 Joules/gram
Slide 18
Energy and Phase Change
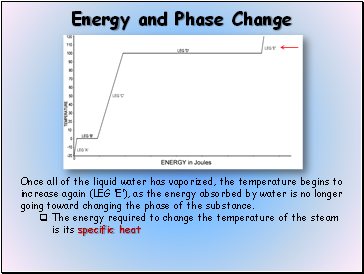
Once all of the liquid water has vaporized, the temperature begins to increase again (LEG E), as the energy absorbed by water is no longer going toward changing the phase of the substance.
The energy required to change the temperature of the steam is its specific heat
Slide 19
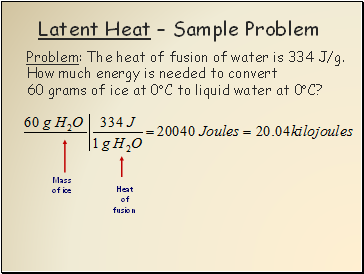
Latent Heat Sample Problem
Problem: The heat of fusion of water is 334 J/g.
How much energy is needed to convert
60 grams of ice at 0C to liquid water at 0C?
Mass
of ice
Heat
of
Contents
- Properties of Water
- Boiling Point and Freezing Point
- Boiling Points for Water at Altitude
- Density
- Waters Thermochemistry
- Units for Measuring Heat
- Specific Heat
- Specific Heat and Climate
- Calculations Involving Specific Heat
- Energy and Phase Change
- Heat of Fusion
- Heat of Vaporization
- Latent Heat Sample Problem
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Madame Marie Curie
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Health Physics
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Newton's Laws