Infectious diseasesPage
3
3
Symptoms: severe diarrhoea up to 20 liters a day of “rice water stool”, vomiting, muscle cramps caused by loss fluid and electrolytes.
Pathogenesis: Vibrio adheres to the small intestinal lining, multiply and produce the enterotoxin choleragen which causes the accumulation of cAMP. An increased secretion of water and electrolyte from the cells results
Slide 21
Cholera
4. Epidemiology: Feacally contaminated water, crabs and vegetables fertilized with human faeces. Has been eradicated most developed countries but a new strain discovered in 1992 is threatening another pandemic.
Slide 22
Cholera
5. Incubation period: 12-48 hours
6. Lab diagnosis: Microscopy, culture of sample from faeces or vomit.
7. Prevention: Purification of water, washing of hands.
8. Treatment: administration of solution of glucose and electrolyte orally or intravenously; tetracycline antibiotic orally
Slide 23
Malaria
Causative Agent: Plasmodium (4 species)
Symptoms (Clinical features): fever, chills, anaemia, headache, nausea, shivering, convulsions (esp. in under 5 yr olds) enlarged spleen.
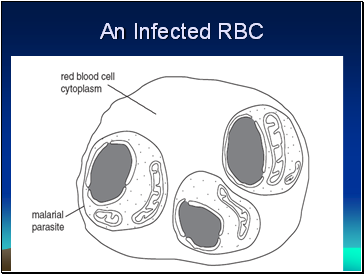
Pathogenesis: site of action of pathogen include: liver, RBC, brain. The vector, female Anopheles mosquito, transfer pathogen during feeding.
Slide 24
malaria
4. Epidemiology: Endemic in 91 tropical and subtropical countries. Invade the liver 1st and move to reproduce in RBCs resulting in their rupture and the associated chills.
5. Incubation Period: 1 – 2 weeks.
6. Lab diagnosis: Microscopy.
Slide 25
An Infected RBC
Slide 26
Malaria - Prevention
Reduce the number of mosquitoes; destruction of larvae and adult mosquitoes by biological and chemical control methods
Avoid being bitten; protective clothing and creams, treated bed nets
Use of drugs to prevent infection; chemoprophylaxis
Slide 27
Malaria -Treatment
Combination therapy: Artesunate Amodiaquine
Slide 28
Tuberculosis
Pathogen: M. tuberculosis (pulmonary TB); M. bovis(GI TB)
Transmission: airborne droplets (NB MTB is dessication resistant and survives in dried sputum); unpasteurized milk.
Clinical features: prolonged coughing sometimes with bloody sputum, shortness of breath, fever, sweating , weight loss
Contents
- Infectious Disease Terms
- Normal Micro flora & its importance
- Koch’s Postulates
- Modifications to Koch’s Postulates
- Types of Pathogens
- Gram Positives
- Gram Negatives
- Types of pathogens
- Viruses
- Modes of transmission
- Pathogenesis
- Virulent Factors
- Bacterial Pathogenesis
- Exotoxins
- Cholera
- Malaria
- Tuberculosis
Last added presentations
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Solar Thermal Energy
- History of Modern Astronomy
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Mechanics Lecture
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Radiation Safety and Operations