Cell membranesPage
3
3
Slide 15
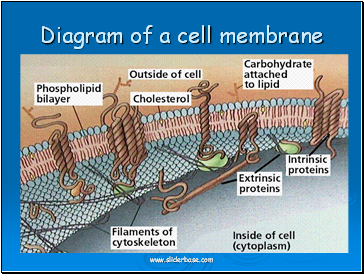
Diagram of a cell membrane
Slide 16
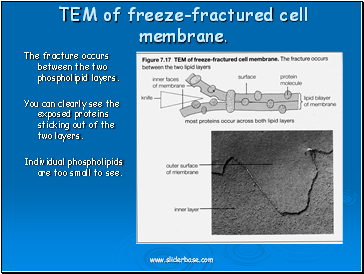
TEM of freeze-fractured cell membrane.
The fracture occurs between the two phospholipid layers.
You can clearly see the exposed proteins sticking out of the two layers.
Individual phospholipids are too small to see.
Slide 17
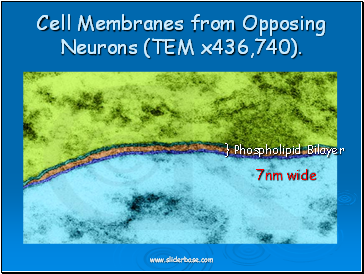
Cell Membranes from Opposing Neurons (TEM x436,740).
} Phospholipid Bilayer
7nm wide
Slide 18
Features of the fluid mosaic model
Double layer BILAYER of phospholipids which can move about by in their own .
Phospholipid tails point inwards forming a . . interior. The phospholipid heads point outwards facing the aqueous (water containing) medium surrounding the membrane.
Some phospholipids fatty acid tails are straight so fit together tightly. Some are bent so fit together . The more unsaturated tails there are the more the membrane becomes. The lower the temp, the .fluid.
Most protein molecules . like icebergs in the layers, some are fixed to . inside the cell and dont float.
Some proteins are embedded in the outer layer, some in the inner layer and some the two layers. Hydrophobic and Hyrdophilic parts of the protein molecules sit next to the and portions of the of the membrane. This ensures the proteins stay in the membrane.
The membrane is nm thick on average.
Some phospholipids have carbohydrates attached to them called-
Some of the proteins have carbohydrates attached to them called
The membrane also contains molecules of
Slide 19
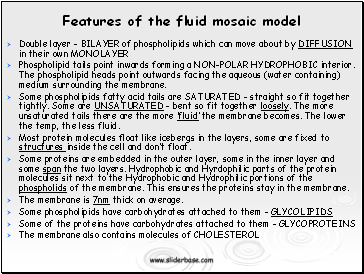
Features of the fluid mosaic model
Double layer BILAYER of phospholipids which can move about by DIFFUSION in their own MONOLAYER
Phospholipid tails point inwards forming a NON-POLAR HYDROPHOBIC interior. The phospholipid heads point outwards facing the aqueous (water containing) medium surrounding the membrane.
Some phospholipids fatty acid tails are SATURATED straight so fit together tightly. Some are UNSATURATED bent so fit together loosely. The more unsaturated tails there are the more fluid the membrane becomes. The lower the temp, the less fluid.
Most protein molecules float like icebergs in the layers, some are fixed to structures inside the cell and dont float.
Some proteins are embedded in the outer layer, some in the inner layer and some span the two layers. Hydrophobic and Hyrdophilic parts of the protein molecules sit next to the Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic portions of the phospholids of the membrane. This ensures the proteins stay in the membrane.
Contents
- Learning Objectives
- Key words you should know
- Cell membrane
- A phospholipid
- 3D model of a Phospholipid
- Structure of the cell membrane
- Fluid mosaic model
- Diagram of a cell membrane
- Features of the fluid mosaic model
- Roles of components of cell membranes
- Summary
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Newtons Law of Gravity
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Radiation
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Newtons law of universal gravitation
- Space Radiation