Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of LifePage
5
5
5-Methyl cytidine is a
component of DNA that has
been modified by addition of
the methyl group.
In addition to taking part in
many important chemical
reactions in cells, glycerol
phosphate provides the
backbone for phospholipids,
the most prevalent molecules in
cell membranes.
Glycerol phosphate
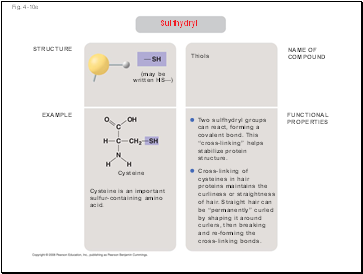
Cysteine
Cysteine is an important
sulfur-containing amino
acid.
Glycine
Because it also has a
carboxyl group, glycine
is both an amine and
a carboxylic acid;
compounds with both
groups are called
amino acids.
Addition of a methyl group
to DNA, or to molecules
bound to DNA, affects
expression of genes.
Arrangement of methyl
groups in male and female
sex hormones affects
their shape and function.
Contributes negative charge
to the molecule of which it is
a part (2– when at the end of
a molecule; 1– when located
internally in a chain of
phosphates).
Has the potential to react
with water, releasing energy.
Two sulfhydryl groups
can react, forming a
covalent bond. This
“cross-linking” helps
stabilize protein
structure.
Cross-linking of
cysteines in hair
proteins maintains the
curliness or straightness
of hair. Straight hair can
be “permanently” curled
by shaping it around
curlers, then breaking
and re-forming the
cross-linking bonds.
Acts as a base; can
pick up an H+ from
the surrounding
solution (water, in
living organisms).
Ionized, with a
charge of 1+, under
cellular conditions.
(nonionized)
(ionized)
Slide 34
Fig. 4-10c
STRUCTURE
EXAMPLE
NAME OF
COMPOUND
FUNCTIONAL
PROPERTIES
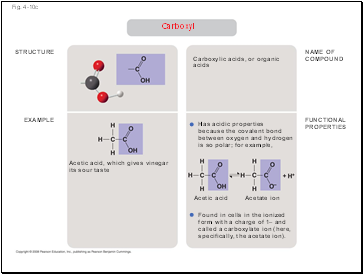
Carboxyl
Acetic acid, which gives vinegar its sour taste
Carboxylic acids, or organic acids
Has acidic properties
because the covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar; for example,
Found in cells in the ionized form with a charge of 1– and called a carboxylate ion (here, specifically, the acetate ion).
Acetic acid
Acetate ion
Slide 35
Fig. 4-10d
STRUCTURE
EXAMPLE
NAME OF
COMPOUND
FUNCTIONAL
PROPERTIES
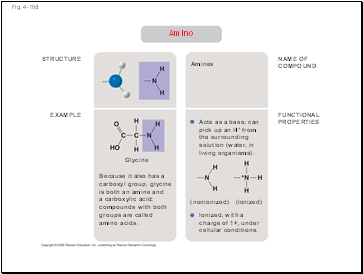
Amino
Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and
a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids.
Amines
Acts as a base; can pick up an H+ from the surrounding solution (water, in living organisms).
Ionized, with a charge of 1+, under cellular conditions.
(ionized)
(nonionized)
Glycine
Slide 36
Fig. 4-10e
STRUCTURE
EXAMPLE
NAME OF
COMPOUND
FUNCTIONAL
Contents
- Carbon: The Backbone of Life
- The Formation of Bonds with Carbon
- Molecular Diversity Arising from Carbon Skeleton Variation
- Hydrocarbons
- Isomers
- The Chemical Groups Most Important in the Processes of Life
- ATP: An Important Source of Energy for Cellular Processes
- The Chemical Elements of Life: A Review
Last added presentations
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Solar Energy
- Sound
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Radiation