Acids, Bases & SaltsPage
3
3
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
Bases are named like any ionic compound, the name of the metal ion first (with a Roman numeral if necessary) followed by “hydroxide”.
Fe(OH)2 (aq) = iron (II) hydroxide
Fe(OH)3 (aq) = iron (III) hydroxide
Al(OH)3 (aq) = aluminum hydroxide
NH3 (aq) is the same thing as NH4OH:
NH3 + H2O NH4OH
Also called ammonium hydroxide.
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
11
Slide 12
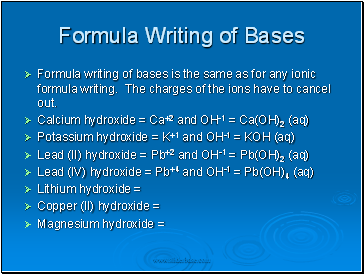
Formula Writing of Bases
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
Formula writing of bases is the same as for any ionic formula writing. The charges of the ions have to cancel out.
Calcium hydroxide = Ca+2 and OH-1 = Ca(OH)2 (aq)
Potassium hydroxide = K+1 and OH-1 = KOH (aq)
Lead (II) hydroxide = Pb+2 and OH-1 = Pb(OH)2 (aq)
Lead (IV) hydroxide = Pb+4 and OH-1 = Pb(OH)4 (aq)
Lithium hydroxide =
Copper (II) hydroxide =
Magnesium hydroxide =
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
12
Slide 13

Physical Properties of Acids & Bases
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
13
ACIDS
Acids taste sour (e.g. vinegar, lemon juice).
Acids are harmful to living cells.
Aqueous solutions of all acids contain hydrogen ions.
Acid turns blue litmus red.
Strong acids are corrosive.
BASES
Alkalis are taste bitter
Strong alkalis are corrosive.
Aqueous solutions of all alkalis contain hydroxide ion.
Alkalis turns red litmus blue.
Soapy touch.
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
Slide 14
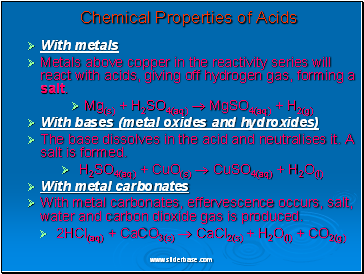
Chemical Properties of Acids
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
14
With metals
Metals above copper in the reactivity series will react with acids, giving off hydrogen gas, forming a salt.
Mg(s) + H2SO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + H2(g)
With bases (metal oxides and hydroxides)
The base dissolves in the acid and neutralises it. A salt is formed.
H2SO4(aq) + CuO(s) CuSO4(aq) + H2O(l)
With metal carbonates
With metal carbonates, effervescence occurs, salt, water and carbon dioxide gas is produced.
2HCl(aq) + CaCO3(s) CaCl2(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
Slide 15
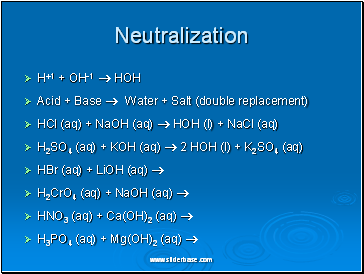
Neutralization
Contents
- TERMS
- Basicity of Acid
- Acidity of a Base
- Common Strong Acids & their Anions
- Common Weak Acids & their Anions
- Naming of Acids
- Formula Writing of Acids
- Properties of Bases
- Naming of Bases
- Formula Writing of Bases
- Physical Properties of Acids & Bases
- Chemical Properties of Acids
- Neutralization
- USES OF ACIDS
- Chemical Properties of Bases
- TYPES OF OXIDES
- SALTS
- Methods of making Soluble Salts
- Making Insoluble Salts
- Types of Salts
- HYDRATED & ANHYDROUS SALTS
- Self Ionization of Water
- pH Graph
- IONIC EQUATIONS
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Sound
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
