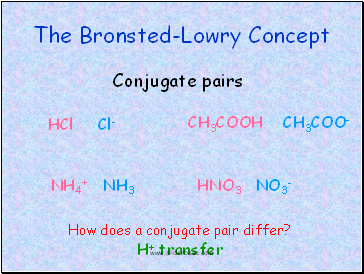Acids and Bases. General propertiesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Acids and Bases
PGCC CHM 101 Sinex
Slide 2
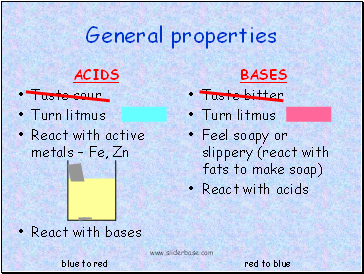
General properties
ACIDS
Taste sour
Turn litmus
React with active metals Fe, Zn
React with bases
BASES
Taste bitter
Turn litmus
Feel soapy or slippery (react with fats to make soap)
React with acids
blue to red
red to blue
Slide 3
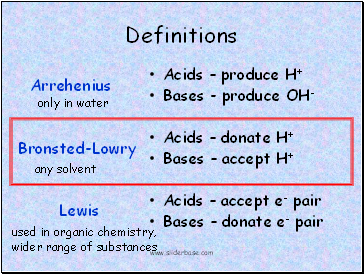
Definitions
Acids produce H+
Bases - produce OH-
Acids donate H+
Bases accept H+
Acids accept e- pair
Bases donate e- pair
Arrehenius
Bronsted-Lowry
Lewis
only in water
any solvent
used in organic chemistry,
wider range of substances
Slide 4
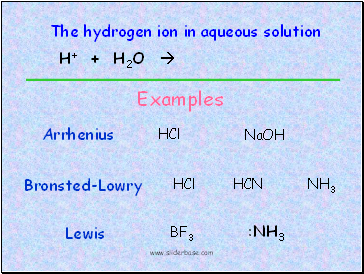
Examples
Arrhenius
Bronsted-Lowry
Lewis
HCl
NaOH
HCl
NH3
:NH3
BF3
HCN
The hydrogen ion in aqueous solution
H+ + H2O H3O+ (hydronium ion)
Slide 5
The Bronsted-Lowry Concept
Conjugate pairs
HCl Cl-
CH3COOH CH3COO-
NH4+ NH3
HNO3 NO3-
How does a conjugate pair differ?
H+ transfer
Slide 6
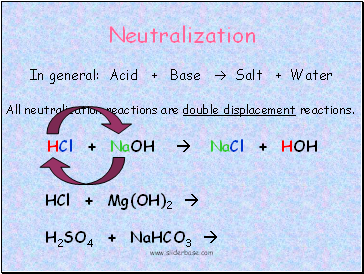
Neutralization
In general: Acid + Base Salt + Water
All neutralization reactions are double displacement reactions.
HCl + NaOH NaCl + HOH
HCl + Mg(OH)2
H2SO4 + NaHCO3
Slide 7
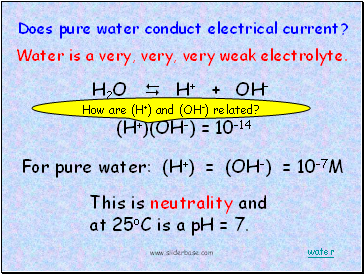
H2O H+ + OH-
Does pure water conduct electrical current?
(H+)(OH-) = 10-14
For pure water: (H+) = (OH-) = 10-7M
This is neutrality and at 25oC is a pH = 7.
Water is a very, very, very weak electrolyte.
How are (H+) and (OH-) related?
water
Slide 8
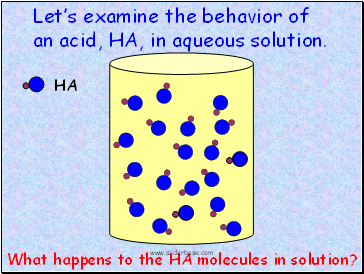
HA
Lets examine the behavior of an acid, HA, in aqueous solution.
What happens to the HA molecules in solution?
Slide 9
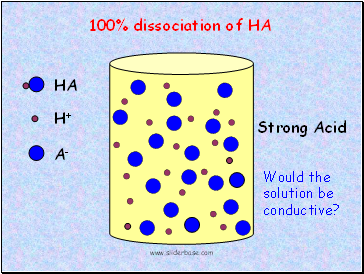
HA
H+
A-
Strong Acid
100% dissociation of HA
Would the solution be conductive?
Slide 10
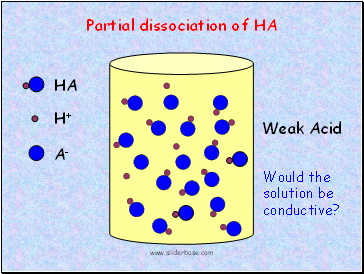
HA
H+
A-
Weak Acid
Partial dissociation of HA
Would the solution be conductive?
Slide 11
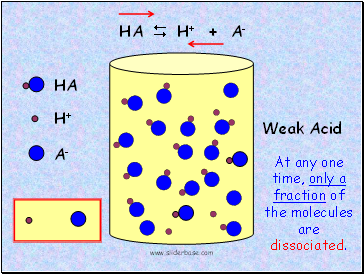
HA
H+
A-
Weak Acid
Contents
- General properties
- Definitions
- The Bronsted-Lowry Concept
- Neutralization
- Strong and Weak Acids/Bases
- What is acid rain?
- Dilution
- Titration Calculation
Last added presentations
- Motion
- Space Radiation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton's laws of motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire