Circulation and Gas ExchangePage
14
14
O2 unloaded
to tissues
at rest
O2 unloaded
to tissues
during exercise
100
40
0
20
60
80
0
40
80
100
O2 saturation of hemoglobin (%)
20
60
Tissues during
exercise
Tissues
at rest
Lungs
PO2 (mm Hg)
(a) PO2 and hemoglobin dissociation at pH 7.4
O2 saturation of hemoglobin (%)
40
0
20
60
80
0
40
80
100
20
60
100
PO2 (mm Hg)
(b) pH and hemoglobin dissociation
pH 7.4
pH 7.2
Hemoglobin
retains less
O2 at lower pH
(higher CO2
concentration)
Slide 89
Carbon Dioxide Transport
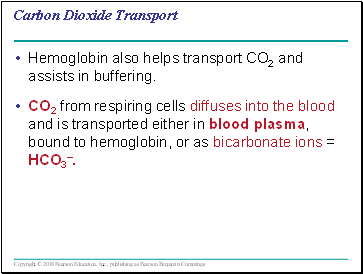
Hemoglobin also helps transport CO2 and assists in buffering.
CO2 from respiring cells diffuses into the blood and is transported either in blood plasma, bound to hemoglobin, or as bicarbonate ions = HCO3–.
Slide 90
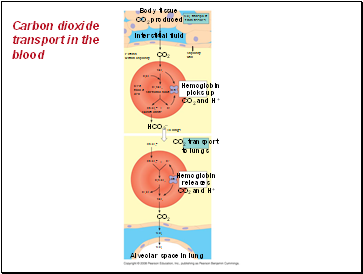
Carbon dioxide transport in the blood
Body tissue
CO2 produced
CO2 transport
from tissues
Capillary
wall
Interstitial fluid
Plasma
within capillary
CO2
CO2
CO2
Red
blood
cell
H2O
H2CO3
Hb
Carbonic acid
Hemoglobin
picks up
CO2 and H+
CO2 transport
to lungs
HCO3–
Bicarbonate
H+
+
Hemoglobin
releases
CO2 and H+
To lungs
HCO3–
HCO3–
Hb
H+
+
HCO3–
H2CO3
H2O
CO2
CO2
CO2
CO2
Alveolar space in lung
Slide 91
Elite Animal Athletes
Migratory and diving mammals have evolutionary adaptations that allow them to perform extraordinary feats.
The extreme O2 consumption of the antelope-like pronghorn underlies its ability to run at high speed over long distances.
Deep-diving air breathers stockpile O2 and deplete it slowly.
Weddell seals have a high blood to body volume ratio and can store oxygen in their muscles in myoglobin proteins.
Slide 92
Review
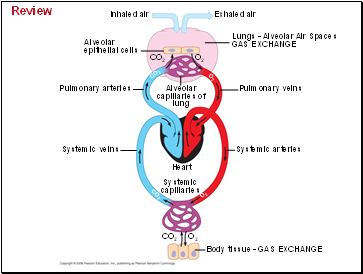
Inhaled air
Exhaled air
Alveolar
epithelial cells
Lungs - Alveolar Air Spaces
GAS EXCHANGE
CO2
O2
CO2
O2
Alveolar
capillaries of
lung
Pulmonary veins
Pulmonary arteries
Systemic veins
Systemic arteries
Heart
Systemic
capillaries
CO2
O2
CO2
O2
Body tissue - GAS EXCHANGE
Slide 93
You should now be able to:
Compare and contrast open and closed circulatory systems.
Compare and contrast the circulatory systems of fish, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals or birds.
Contents
- Trading Places
- Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body
- Gastrovascular Cavities
- Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
- Organization of Vertebrate Closed Circulatory Systems
- Single Circulation
- Double Circulation
- Adaptations of Double Circulatory Systems
- Coordinated cycles of heart contraction drive double circulation in mammals
- The Mammalian Heart: A Closer Look
- Maintaining the Heart’s Rhythic Beat
- Patterns of blood pressure and flow reflect the structure and arrangement of blood vessels
- Blood Flow Velocity
- Blood Pressure
- Regulation of Blood Pressure
- Capillary Function
- Fluid Return by the Lymphatic System
- Blood Composition and Function
- Cardiovascular Disease = Disorders of the Heart and the Blood Vessels
- Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces
- Respiratory Media
- Respiratory Surfaces
- Tracheal Systems in Insects
- Lungs = Infoldings of the body surface
- How a Bird Breathes
- Control of Breathing in Humans
- Adaptations for gas exchange include pigments that bind and transport gases
- Respiratory Pigments
- Elite Animal Athletes
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radiation
- Sound
- Solar Energy