Circulation and Gas ExchangePage
13
13
The pons regulates the tempo.
Slide 81
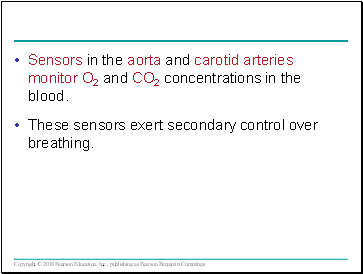
Sensors in the aorta and carotid arteries monitor O2 and CO2 concentrations in the blood.
These sensors exert secondary control over breathing.
Slide 82
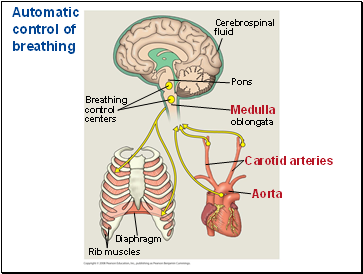
Automatic control of breathing
Breathing
control
centers
Cerebrospinal
fluid
Pons
Medulla
oblongata
Carotid arteries
Aorta
Diaphragm
Rib muscles
Slide 83
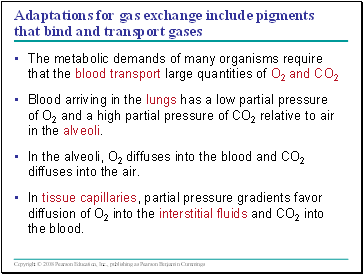
Adaptations for gas exchange include pigments that bind and transport gases
The metabolic demands of many organisms require that the blood transport large quantities of O2 and CO2
Blood arriving in the lungs has a low partial pressure of O2 and a high partial pressure of CO2 relative to air in the alveoli.
In the alveoli, O2 diffuses into the blood and CO2 diffuses into the air.
In tissue capillaries, partial pressure gradients favor diffusion of O2 into the interstitial fluids and CO2 into the blood.
Slide 84
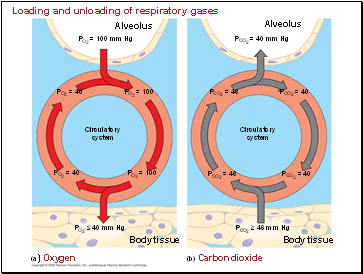
Loading and unloading of respiratory gases
Alveolus
PO2 = 100 mm Hg
PO2 = 40
PO2 = 100
PO2 = 100
PO2 = 40
Circulatory
system
Body tissue
PO2 ≤ 40 mm Hg
PCO2 ≥ 46 mm Hg
Body tissue
PCO2 = 46
PCO2 = 40
PCO2 = 40
PCO2 = 46
Circulatory
system
PCO2 = 40 mm Hg
Alveolus
(b) Carbon dioxide
(a) Oxygen
Slide 85
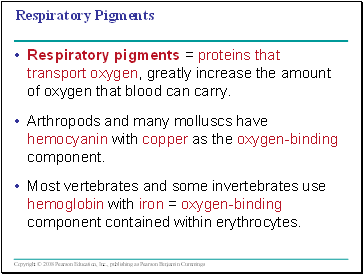
Respiratory Pigments
Respiratory pigments = proteins that transport oxygen, greatly increase the amount of oxygen that blood can carry.
Arthropods and many molluscs have hemocyanin with copper as the oxygen-binding component.
Most vertebrates and some invertebrates use hemoglobin with iron = oxygen-binding component contained within erythrocytes.
Slide 86
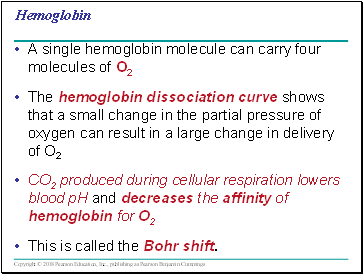
Hemoglobin
A single hemoglobin molecule can carry four molecules of O2
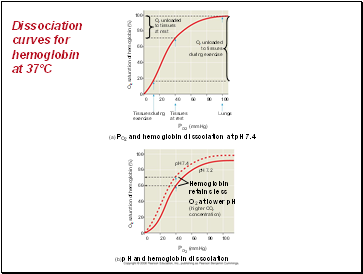
The hemoglobin dissociation curve shows that a small change in the partial pressure of oxygen can result in a large change in delivery of O2
CO2 produced during cellular respiration lowers blood pH and decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2
This is called the Bohr shift.
Slide 87
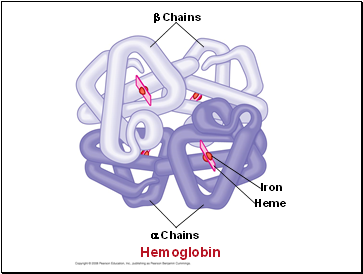
Chains
Iron
Heme
Chains
Hemoglobin
Slide 88
Dissociation curves for hemoglobin at 37ºC
Contents
- Trading Places
- Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body
- Gastrovascular Cavities
- Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
- Organization of Vertebrate Closed Circulatory Systems
- Single Circulation
- Double Circulation
- Adaptations of Double Circulatory Systems
- Coordinated cycles of heart contraction drive double circulation in mammals
- The Mammalian Heart: A Closer Look
- Maintaining the Heart’s Rhythic Beat
- Patterns of blood pressure and flow reflect the structure and arrangement of blood vessels
- Blood Flow Velocity
- Blood Pressure
- Regulation of Blood Pressure
- Capillary Function
- Fluid Return by the Lymphatic System
- Blood Composition and Function
- Cardiovascular Disease = Disorders of the Heart and the Blood Vessels
- Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces
- Respiratory Media
- Respiratory Surfaces
- Tracheal Systems in Insects
- Lungs = Infoldings of the body surface
- How a Bird Breathes
- Control of Breathing in Humans
- Adaptations for gas exchange include pigments that bind and transport gases
- Respiratory Pigments
- Elite Animal Athletes
Last added presentations
- Health Physics
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Upcoming Classes
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Solar Thermal Energy