Circulation and Gas ExchangePage
11
11
Respiratory surfaces vary by animal and can include the outer surface, skin, gills, tracheae, and lungs.
Slide 68
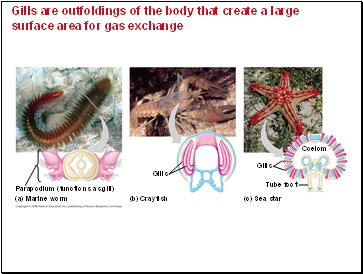
Gills are outfoldings of the body that create a large surface area for gas exchange
Parapodium (functions as gill)
(a) Marine worm
Gills
(b) Crayfish
(c) Sea star
Tube foot
Coelom
Gills
Slide 69
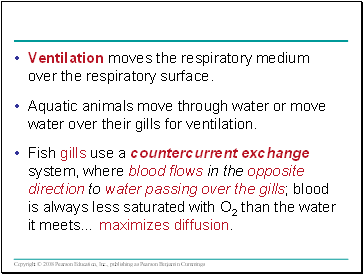
Ventilation moves the respiratory medium over the respiratory surface.
Aquatic animals move through water or move water over their gills for ventilation.
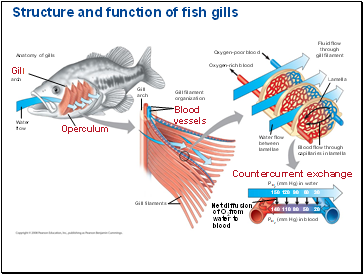
Fish gills use a countercurrent exchange system, where blood flows in the opposite direction to water passing over the gills; blood is always less saturated with O2 than the water it meets… maximizes diffusion.
Slide 70
Structure and function of fish gills
Anatomy of gills
Gill
arch
Water
flow
Operculum
Gill
arch
Gill filament
organization
Blood
vessels
Oxygen-poor blood
Oxygen-rich blood
Fluid flow
through
gill filament
Lamella
Blood flow through
capillaries in lamella
Water flow
between
lamellae
Countercurrent exchange
PO2 (mm Hg) in water
PO2 (mm Hg) in blood
Net diffusion
of O2from
water to
blood
150
120
90
60
30
110
80
20
Gill filaments
50
140
Slide 71
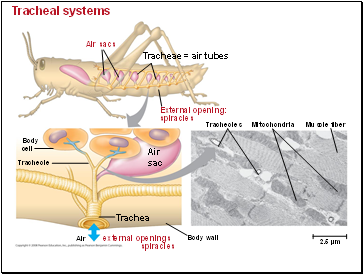
Tracheal Systems in Insects
The tracheal system of insects consists of tiny branching tubes that penetrate the body.
The tracheal tubes supply O2 directly to body cells.
The respiratory and circulatory systems are separate.
Larger insects must ventilate their tracheal system to meet O2 demands.
Slide 72
Tracheal systems
Air sacs
Tracheae = air tubes
External opening:
spiracles
Body
cell
Air
sac
Tracheole
Tracheoles
Mitochondria
Muscle fiber
2.5 µm
Body wall
Trachea
Air external openings
spiracles
Slide 73
Lungs = Infoldings of the body surface
The circulatory system (open or closed) transports gases between the lungs and the rest of the body.
The size and complexity of lungs correlate with an animal’s metabolic rate.
Slide 74
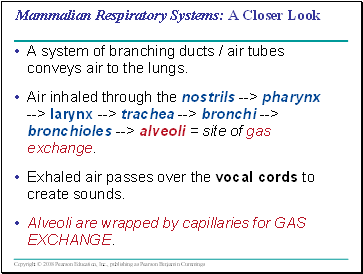
Mammalian Respiratory Systems: A Closer Look
A system of branching ducts / air tubes conveys air to the lungs.
Air inhaled through the nostrils --> pharynx --> larynx --> trachea --> bronchi --> bronchioles --> alveoli = site of gas exchange.
Contents
- Trading Places
- Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body
- Gastrovascular Cavities
- Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
- Organization of Vertebrate Closed Circulatory Systems
- Single Circulation
- Double Circulation
- Adaptations of Double Circulatory Systems
- Coordinated cycles of heart contraction drive double circulation in mammals
- The Mammalian Heart: A Closer Look
- Maintaining the Heart’s Rhythic Beat
- Patterns of blood pressure and flow reflect the structure and arrangement of blood vessels
- Blood Flow Velocity
- Blood Pressure
- Regulation of Blood Pressure
- Capillary Function
- Fluid Return by the Lymphatic System
- Blood Composition and Function
- Cardiovascular Disease = Disorders of the Heart and the Blood Vessels
- Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces
- Respiratory Media
- Respiratory Surfaces
- Tracheal Systems in Insects
- Lungs = Infoldings of the body surface
- How a Bird Breathes
- Control of Breathing in Humans
- Adaptations for gas exchange include pigments that bind and transport gases
- Respiratory Pigments
- Elite Animal Athletes
Last added presentations
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Motion
- Waves & Sound
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Madame Marie Curie