InvertebratesPage
6
6
Mouth
Anus
Mantle
cavity
Stomach
Intestine
Slide 50
Bivalves
Molluscs of class Bivalvia include many species of clams, oysters, mussels, and scallops.
They have a shell divided into two halves.
Slide 51
Bivalve
Slide 52
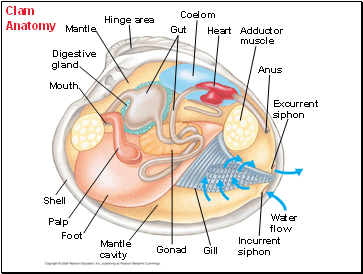
The mantle cavity of a bivalve contains gills that are used for feeding as well as gas exchange.
Slide 53
Clam Anatomy
Mouth
Digestive
gland
Mantle
Hinge area
Gut
Coelom
Heart
Adductor
muscle
Anus
Excurrent
siphon
Water
flow
Incurrent
siphon
Gill
Gonad
Mantle
cavity
Foot
Palp
Shell
Slide 54
Cephalopods
Class Cephalopoda includes squids and octopuses, carnivores with beak-like jaws surrounded by tentacles of their modified foot.
Most octopuses creep along the sea floor in search of prey.
Slide 55
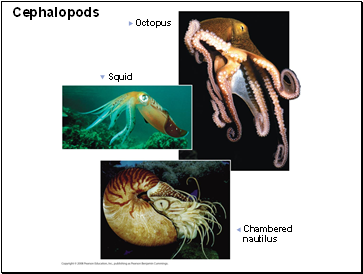
Cephalopods
Octopus
Squid
Chambered
nautilus
Slide 56
Squids use their siphon to fire a jet of water, which allows them to swim very quickly.
Squid
Slide 57
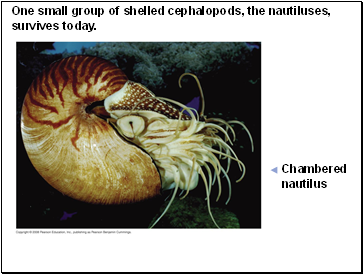
One small group of shelled cephalopods, the nautiluses, survives today.
Chambered
nautilus
Slide 58
Cephalopods have a closed circulatory system, well-developed sense organs, and a complex brain.
Shelled cephalopods called ammonites were common but went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous.
Slide 59
Annelids
Annelids have bodies composed of a series of fused rings.
The phylum Annelida is divided into three classes:
Oligochaeta (earthworms and their relatives)
Polychaeta (polychaetes)
Hirudinea (leeches)
Slide 60
Oligochaetes
Oligochaetes (class Oligochaeta) are named for relatively sparse chaetae, bristles made of chitin.
They include the earthworms and a variety of aquatic species.
Earthworms eat through soil, extracting nutrients as the soil moves through the alimentary canal.
Earthworms are hermaphrodites but cross-fertilize.
Contents
- Life Without a Backbone
- Scyphozoans
- Cubozoans
- Anthozoans
- Flatworms
- Tapeworms
- Rotifers
- Lophophorates: Ectoprocts and Brachiopods
- Molluscs
- Gastropods
- Bivalves
- Cephalopods
- Annelids
- Oligochaetes
- Leeches
- Nematodes
- Arthropods
- Myriapods
- Insects
- Crustaceans
- Echinoderms
- Sea Stars
- Sea Cucumbers
- Chordates
Last added presentations
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Gravitation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Newton's Laws