InvertebratesPage
3
3
Portion of
a colony
of polyps
1 mm
Key
Haploid (n)
Diploid (2n)
Slide 20
Fig. 33-8-2
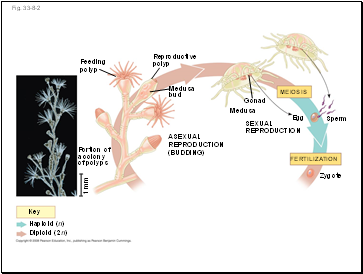
Feeding
polyp
Reproductive
polyp
Medusa
bud
Medusa
ASEXUAL
REPRODUCTION
(BUDDING)
Portion of
a colony
of polyps
1 mm
Key
Haploid (n)
Diploid (2n)
Gonad
SEXUAL
REPRODUCTION
MEIOSIS
FERTILIZATION
Egg
Sperm
Zygote
Slide 21
Fig. 33-8-3
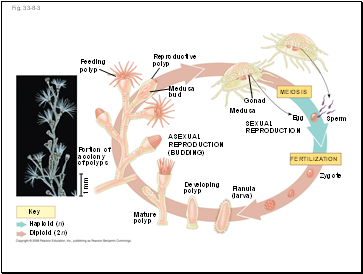
Feeding
polyp
Reproductive
polyp
Medusa
bud
Medusa
ASEXUAL
REPRODUCTION
(BUDDING)
Portion of
a colony
of polyps
1 mm
Key
Haploid (n)
Diploid (2n)
Gonad
SEXUAL
REPRODUCTION
MEIOSIS
FERTILIZATION
Egg
Sperm
Zygote
Planula
(larva)
Developing
polyp
Mature
polyp
Slide 22
Scyphozoans
In the class Scyphozoa, jellies (medusae) are the prevalent form of the life cycle
Slide 23
Cubozoans
In the class Cubozoa, which includes box jellies and sea wasps, the medusa is box-shaped and has complex eyes.
Cubozoans often have highly toxic cnidocytes.
Slide 24
Anthozoans
Class Anthozoa includes the corals and sea anemones, which occur only as polyps.
Slide 25
Concept 33.3: Lophotrochozoans, a clade identified by molecular data, have the widest range of animal body forms
Bilaterian animals have bilateral symmetry and triploblastic development.
The clade Bilateria contains Lophotrochozoa, Ecdysozoa, and Deuterostomia.
Slide 26
Fig. 33-UN3 Lophotrochozoa includes the flatworms, rotifers, ectoprocts, brachiopods, molluscs, and annelids
Calcarea and Silicea
Cnidaria
Lophotrochozoa
Ecdysozoa
Deuterostomia
Slide 27
Flatworms
Members of phylum Platyhelminthes live in marine, freshwater, and damp terrestrial habitats.
Although flatworms undergo triploblastic development, they are acoelomates.
They are flattened dorsoventrally and have a gastrovascular cavity.
Gas exchange takes place across the surface, and protonephridia regulate the osmotic balance.
Slide 28
Flatworms are divided into four classes:
Contents
- Life Without a Backbone
- Scyphozoans
- Cubozoans
- Anthozoans
- Flatworms
- Tapeworms
- Rotifers
- Lophophorates: Ectoprocts and Brachiopods
- Molluscs
- Gastropods
- Bivalves
- Cephalopods
- Annelids
- Oligochaetes
- Leeches
- Nematodes
- Arthropods
- Myriapods
- Insects
- Crustaceans
- Echinoderms
- Sea Stars
- Sea Cucumbers
- Chordates
Last added presentations
- Upcoming Classes
- Mechanics Lecture
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Radiation
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Madame Marie Curie