Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesPage
4
4
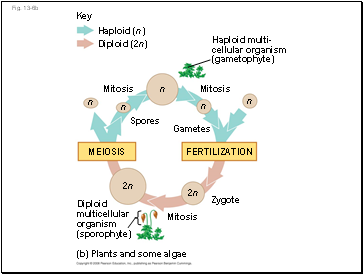
Each spore grows by mitosis into a haploid organism called a gametophyte
A gametophyte makes haploid gametes by mitosis
Fertilization of gametes results in a diploid sporophyte
Slide 28
Fig. 13-6b
Key
Haploid (n)
Diploid (2n)
n
n
n
n
n
2n
2n
Mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis
Zygote
Spores
Gametes
MEIOSIS
FERTILIZATION
Diploid
multicellular
organism
(sporophyte)
Haploid multi-
cellular organism
(gametophyte)
(b) Plants and some algae
Slide 29
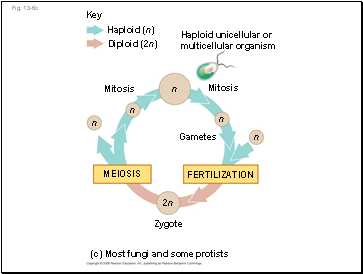
In most fungi and some protists, the only diploid stage is the single-celled zygote; there is no multicellular diploid stage
The zygote produces haploid cells by meiosis
Each haploid cell grows by mitosis into a haploid multicellular organism
The haploid adult produces gametes by mitosis
Slide 30
Fig. 13-6c
Key
Haploid (n)
Diploid (2n)
Mitosis
Mitosis
Gametes
Zygote
Haploid unicellular or
multicellular organism
MEIOSIS
FERTILIZATION
n
n
n
n
n
2n
(c) Most fungi and some protists
Slide 31
Depending on the type of life cycle, either haploid or diploid cells can divide by mitosis
However, only diploid cells can undergo meiosis
In all three life cycles, the halving and doubling of chromosomes contributes to genetic variation in offspring
Slide 32
Concept 13.3: Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from diploid to haploid
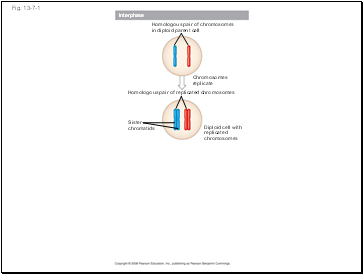
Like mitosis, meiosis is preceded by the replication of chromosomes
Meiosis takes place in two sets of cell divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
The two cell divisions result in four daughter cells, rather than the two daughter cells in mitosis
Each daughter cell has only half as many chromosomes as the parent cell
Slide 33
The Stages of Meiosis
In the first cell division (meiosis I), homologous chromosomes separate
Meiosis I results in two haploid daughter cells with replicated chromosomes; it is called the reductional division
In the second cell division (meiosis II), sister chromatids separate
Meiosis II results in four haploid daughter cells with unreplicated chromosomes; it is called the equational division
Slide 34
Fig. 13-7-1
Interphase
Homologous pair of chromosomes
Contents
- Variations on a Theme
- Inheritance of Genes
- Comparison of Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
- Sets of Chromosomes in Human Cells
- Fertilization is the union of gametes (the sperm and the egg)
- The Variety of Sexual Life Cycles
- The Stages of Meiosis
- A Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis
- Origins of Genetic Variation Among Offspring
- Independent Assortment of Chromosomes
- Crossing Over
- Random Fertilization
- The Evolutionary Significance of Genetic Variation Within Populations
Last added presentations
- Madame Marie Curie
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Space Radiation
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Solar Energy