Membrane Structure and FunctionPage
5
5
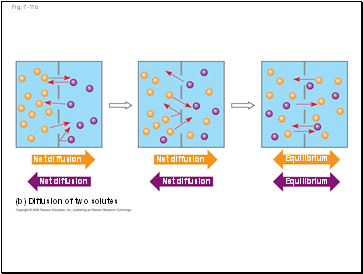
Substances diffuse down their concentration gradient, the difference in concentration of a substance from one area to another
No work must be done to move substances down the concentration gradient
The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane is passive transport because it requires no energy from the cell to make it happen
Slide 37
(b) Diffusion of two solutes
Fig. 7-11b
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Equilibrium
Equilibrium
Slide 38
Effects of Osmosis on Water Balance
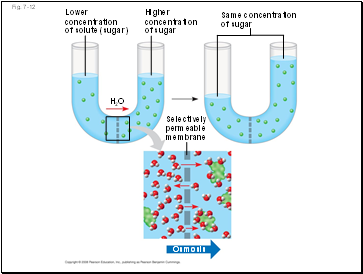
Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Water diffuses across a membrane from the region of lower solute concentration to the region of higher solute concentration
Slide 39
Lower
concentration
of solute (sugar)
Fig. 7-12
H2O
Higher concentration
of sugar
Selectively
permeable
membrane
Same concentration
of sugar
Osmosis
Slide 40
Water Balance of Cells Without Walls
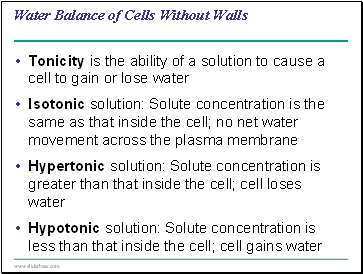
Tonicity is the ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Isotonic solution: Solute concentration is the same as that inside the cell; no net water movement across the plasma membrane
Hypertonic solution: Solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell; cell loses water
Hypotonic solution: Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
Slide 41
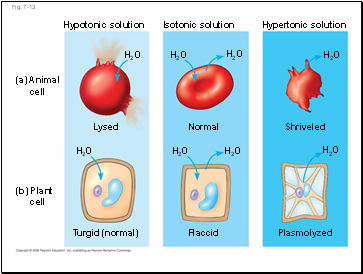
Fig. 7-13
Hypotonic solution
(a) Animal
cell
(b) Plant
cell
H2O
Lysed
H2O
Turgid (normal)
H2O
H2O
H2O
H2O
Normal
Isotonic solution
Flaccid
H2O
H2O
Shriveled
Plasmolyzed
Hypertonic solution
Slide 42
Hypertonic or hypotonic environments create osmotic problems for organisms
Osmoregulation, the control of water balance, is a necessary adaptation for life in such environments
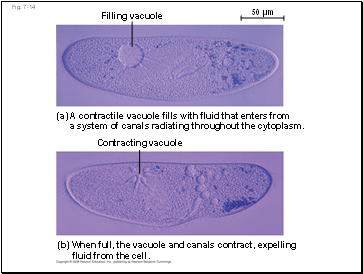
The protist Paramecium, which is hypertonic to its pond water environment, has a contractile vacuole that acts as a pump
Video: Chlamydomonas
Video: Paramecium Vacuole
Slide 43
Fig. 7-14
Filling vacuole
50 µm
(a) A contractile vacuole fills with fluid that enters from
a system of canals radiating throughout the cytoplasm.
Contracting vacuole
(b) When full, the vacuole and canals contract, expelling
Contents
- Life at the Edge
- Membrane Models: Scientific Inquiry
- The Fluidity of Membranes
- Membrane Proteins and Their Functions
- The Role of Membrane Carbohydrates in Cell-Cell Recognition
- Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes
- The Permeability of the Lipid Bilayer
- Transport Proteins
- Effects of Osmosis on Water Balance
- Water Balance of Cells with Walls
- Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided by Proteins
- The Need for Energy in Active Transport
- How Ion Pumps Maintain Membrane Potential
- Cotransport: Coupled Transport by a Membrane Protein
- Exocytosis
- Endocytosis
Last added presentations
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Health Physics
- Friction
- Newton's Laws
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Gravitation