Membrane Structure and FunctionPage
4
4
Fig. 7-10
ER
1
Transmembrane
glycoproteins
Secretory
protein
Glycolipid
2
Golgi
apparatus
Vesicle
3
4
Secreted
protein
Transmembrane
glycoprotein
Plasma membrane:
Cytoplasmic face
Extracellular face
Membrane glycolipid
Slide 29
Concept 7.2: Membrane structure results in selective permeability
A cell must exchange materials with its surroundings, a process controlled by the plasma membrane
Plasma membranes are selectively permeable, regulating the cell’s molecular traffic
Slide 30
The Permeability of the Lipid Bilayer
Hydrophobic (nonpolar) molecules, such as hydrocarbons, can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and pass through the membrane rapidly
Polar molecules, such as sugars, do not cross the membrane easily
Slide 31
Transport Proteins
Transport proteins allow passage of hydrophilic substances across the membrane
Some transport proteins, called channel proteins, have a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or ions can use as a tunnel
Channel proteins called aquaporins facilitate the passage of water
Slide 32
Other transport proteins, called carrier proteins, bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane
A transport protein is specific for the substance it moves
Slide 33
Concept 7.3: Passive transport is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment
Diffusion is the tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space
Although each molecule moves randomly, diffusion of a population of molecules may exhibit a net movement in one direction
At dynamic equilibrium, as many molecules cross one way as cross in the other direction
Animation: Membrane Selectivity
Animation: Diffusion
Slide 34
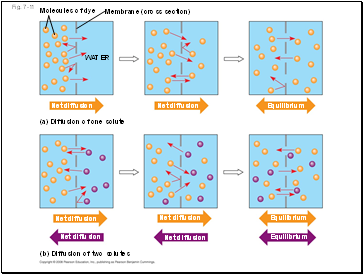
Fig. 7-11
Molecules of dye
Membrane (cross section)
WATER
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Equilibrium
(a) Diffusion of one solute
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Equilibrium
Equilibrium
(b) Diffusion of two solutes
Slide 35
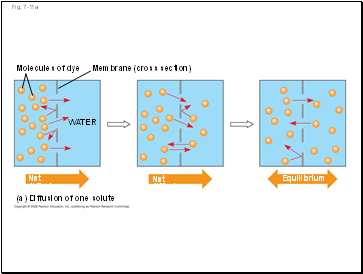
Molecules of dye
Fig. 7-11a
Membrane (cross section)
WATER
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
(a) Diffusion of one solute
Equilibrium
Slide 36
Contents
- Life at the Edge
- Membrane Models: Scientific Inquiry
- The Fluidity of Membranes
- Membrane Proteins and Their Functions
- The Role of Membrane Carbohydrates in Cell-Cell Recognition
- Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes
- The Permeability of the Lipid Bilayer
- Transport Proteins
- Effects of Osmosis on Water Balance
- Water Balance of Cells with Walls
- Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided by Proteins
- The Need for Energy in Active Transport
- How Ion Pumps Maintain Membrane Potential
- Cotransport: Coupled Transport by a Membrane Protein
- Exocytosis
- Endocytosis
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Buoyancy
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Space Radiation
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations