Membrane Structure and FunctionPage
2
2
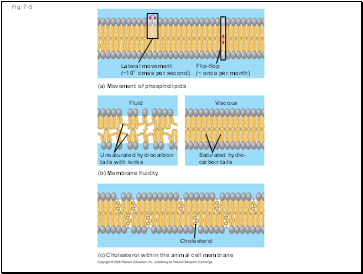
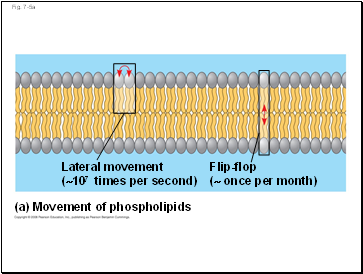
Most of the lipids, and some proteins, drift laterally
Rarely does a molecule flip-flop transversely across the membrane
Slide 11
Fig. 7-5
Lateral movement
(~107 times per second)
Flip-flop
(~ once per month)
(a) Movement of phospholipids
(b) Membrane fluidity
Fluid
Viscous
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
tails with kinks
Saturated hydro-
carbon tails
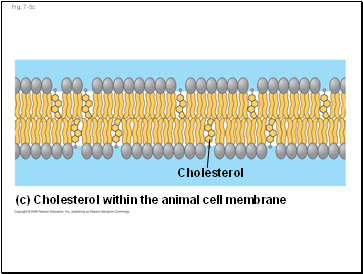
(c) Cholesterol within the animal cell membrane
Cholesterol
Slide 12
Fig. 7-5a
(a) Movement of phospholipids
Lateral movement
(107 times per second)
Flip-flop
( once per month)
Slide 13
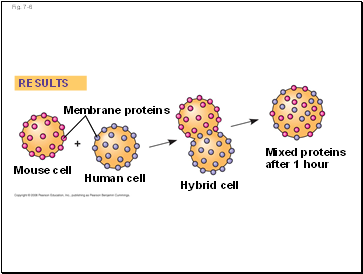
Fig. 7-6
RESULTS
Membrane proteins
Mouse cell
Human cell
Hybrid cell
Mixed proteins
after 1 hour
Slide 14
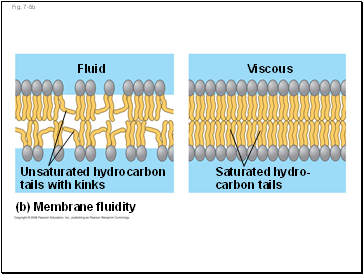
As temperatures cool, membranes switch from a fluid state to a solid state
The temperature at which a membrane solidifies depends on the types of lipids
Membranes rich in unsaturated fatty acids are more fluid that those rich in saturated fatty acids
Membranes must be fluid to work properly; they are usually about as fluid as salad oil
Slide 15
Fig. 7-5b
(b) Membrane fluidity
Fluid
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
tails with kinks
Viscous
Saturated hydro-
carbon tails
Slide 16
The steroid cholesterol has different effects on membrane fluidity at different temperatures
At warm temperatures (such as 37°C), cholesterol restrains movement of phospholipids
At cool temperatures, it maintains fluidity by preventing tight packing
Slide 17
Fig. 7-5c
Cholesterol
(c) Cholesterol within the animal cell membrane
Slide 18
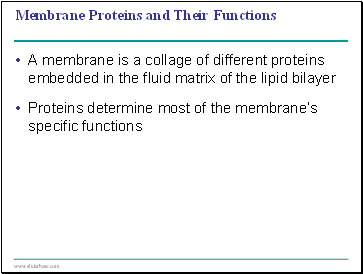
Membrane Proteins and Their Functions
A membrane is a collage of different proteins embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer
Proteins determine most of the membrane’s specific functions
Slide 19
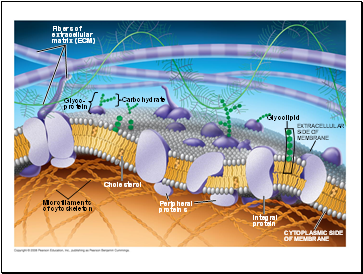
Fig. 7-7
Fibers of
extracellular
matrix (ECM)
Glyco-
protein
Microfilaments
of cytoskeleton
Cholesterol
Peripheral
proteins
Integral
protein
CYTOPLASMIC SIDE
OF MEMBRANE
Glycolipid
EXTRACELLULAR
SIDE OF
Contents
- Life at the Edge
- Membrane Models: Scientific Inquiry
- The Fluidity of Membranes
- Membrane Proteins and Their Functions
- The Role of Membrane Carbohydrates in Cell-Cell Recognition
- Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes
- The Permeability of the Lipid Bilayer
- Transport Proteins
- Effects of Osmosis on Water Balance
- Water Balance of Cells with Walls
- Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided by Proteins
- The Need for Energy in Active Transport
- How Ion Pumps Maintain Membrane Potential
- Cotransport: Coupled Transport by a Membrane Protein
- Exocytosis
- Endocytosis
Last added presentations
- Space Radiation
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Motion
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Friction
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Sound