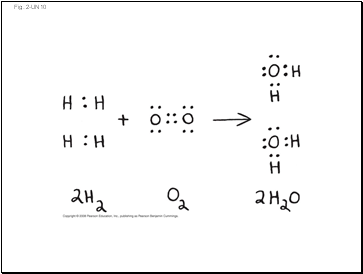
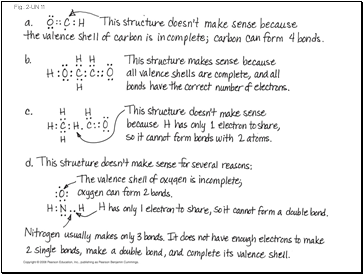
The Chemical Context of LifePage
11
11
Arthropod exoskeletons are made of cuticle and can be both strong and flexible.
The polysaccharide chitin is often found in arthropod cuticle.
Slide 79
Endoskeletons
An endoskeleton consists of hard supporting elements, such as bones, buried in soft tissue
Endoskeletons are found in sponges, echinoderms, and chordates.
A mammalian skeleton has more than 200 bones.
Some bones are fused; others are connected at joints by ligaments that allow freedom of movement.
Slide 80
Bones and joints of the human skeleton
Examples of joints
Humerus
Ball-and-socket joint
Radius
Scapula
Head of humerus
Ulna
Hinge joint
Ulna
Pivot joint
Skull
Shoulder girdle
Rib
Sternum
Clavicle
Scapula
Vertebra
Humerus
Phalanges
Radius
Pelvic girdle
Ulna
Carpals
Metacarpals
Femur
Patella
Tibia
Fibula
Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges
1
1
2
3
3
2
Slide 81
Types of Locomotion
Most animals are capable of locomotion, or active travel from place to place.
In locomotion, energy is expended to overcome friction and gravity.
In water, friction is a bigger problem than gravity. Fast swimmers usually have a streamlined shape to minimize friction.
Slide 82
Locomotion on Land
Walking, running, hopping, or crawling on land requires an animal to support itself and move against gravity.
Diverse adaptations for locomotion on land have evolved in vertebrates.
Slide 83
Energy-efficient locomotion on land
Slide 84
Flying
Flight requires that wings develop enough lift to overcome the downward force of gravity.
Many flying animals have adaptations that reduce body mass.
For example, birds lack teeth and a urinary bladder
Slide 85
What are the energy costs of locomotion?
Body mass (g)
Running
Swimming
Flying
Energy cost (cal/kg•m)
102
103
10
1
10–1
10–3
106
1
RESULTS
Slide 86
You should now be able to:
Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: sensation and perception; sensory transduction and receptor potential; tastants and odorants; rod and cone cells; oxidative and glycolytic muscle fibers; slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers; endoskeleton and exoskeleton.
Contents
- Sensing and Acting
- Sensory Pathways
- Types of Sensory Receptors
- Electromagnetic Receptors
- Thermoreceptors & Pain Receptors
- Sensing Gravity and Sound in Invertebrates
- Hearing and Equilibrium in Mammals
- Hearing
- Equilibrium
- Hearing and Equilibrium in Other Vertebrates
- The senses of taste and smell rely on similar sets of sensory receptors
- Taste in Mammals
- Smell in Humans
- Similar mechanisms underlie vision throughout the animal kingdom
- Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle
- Other Types of Muscle
- Skeletal systems transform muscle contraction into locomotion
- Types of Skeletal Systems
- Types of Locomotion
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Friction
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Newton's Laws
- Radiation Safety and Operations