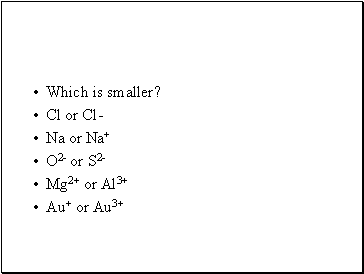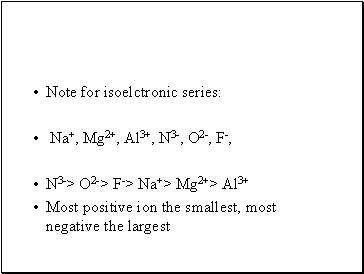Periodictable - QuestionsPage
6
6
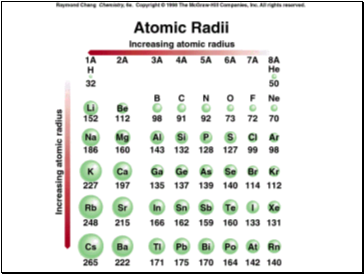
So atomic radius (size) determined by:
1. Larger value of n for atom in a group, the larger the atom size. Size _ from top to bottom in group.
Slide 54
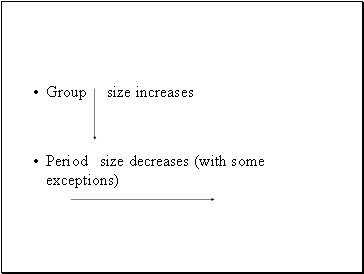
Size across a period
As go across a period (n stays the same), the no. of protons in the nucleus increases. The e’s are very spread out and each electron feels the pull of the increasing +charge of the nucleus uninfluenced by the other electrons and size as go from left to right across a period.
Slide 55
Slide 56
Group size increases
Period size decreases (with some exceptions)
Slide 57
Slide 58
3.62; Arrange each of the lists according to increasing atomic size:
Al, S, P, Cl, Si
In, Ga, Al, B, Tl
Sr, Ca, Ba, Mg, Be
P, N, Sb, Bi, As
Na, K, Mg
Slide 59
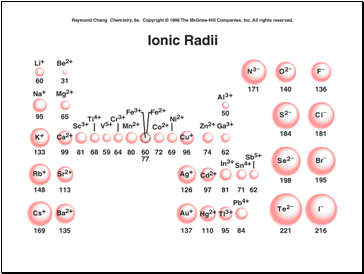
Ion size
Same charge, in group, size creases
Size of parent to cation:
Parent cation
Size of parent to anion:
Parent anion
Fe2+ Fe3+
Slide 60
Which is smaller?
Cl or Cl-
Na or Na+
O2- or S2-
Mg2+ or Al3+
Au+ or Au3+
Slide 61
Slide 62
Note for isoelctronic series:
Na+, Mg2+, Al3+, N3-, O2-, F-,
N3-> O2-> F-> Na+> Mg2+> Al3+
Most positive ion the smallest, most negative the largest
Slide 63
Ionization energy
Minimum energy required to remove an electron from a ground-state, gaseous atom
Energy always positive (requires energy)
Measures how tightly the e- is held in atom (think size also)
Energy associated with this reaction:
Slide 64
Trends in ionization energy
Top to bottom in group: 1st I.E. creases. Why?
Across a period, 1st I.E. creases (irregularly) Why? Note that noble gases have the largest I.E. in a given period; the halogens the next highest; the alkali metals the lowest, etc.
Slide 65
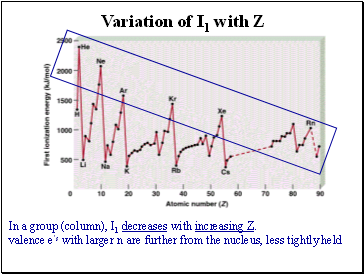
In a group (column), I1 decreases with increasing Z.
valence e’s with larger n are further from the nucleus, less tightly held
Contents
- Elements, atoms, ions, and the periodic table
- The periodic law and the periodic table
- Early periodic tables
- Modern periodic table
- Metals and nonmetals
- More info from periodic table
- Electron arrangement and the periodic table
- Principal energy levels (shells)
- Sublevels
- Orbitals
- Electron spin
- What to do with all this info?
- Abbreviated electron configuration
- Valence electrons
- Valence electron configuration for A groups
- The octet rule
- Transition metal cations
- What’s the ion formed by
- Isoelectronic
- Trends in the periodic table
- Size across a period
- Ion size
- Ionization energy
- Trends in ionization energy
- Electron affinity
- Trends in electron affinities
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Upcoming Classes
- Health Physics
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Space Radiation
- Madame Marie Curie