VolumetricPage
5
5
Rinse the burette and the pipette with the solutions to be used in them, to avoid dilution with water.
The burette tap must be tight to avoid leakage.
Remove the funnel from the burette before titration, to avoid an increase in the volume of the solution in the burette.
CONSULT YOUR TEXTBOOKS FOR MORE PRECAUTIONS
Slide 34
Recording in titration
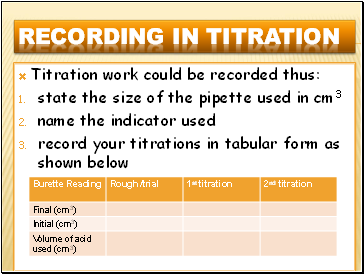
Titration work could be recorded thus:
state the size of the pipette used in cm3
name the indicator used
record your titrations in tabular form as shown below
Slide 35
Find the average volume of acid used from any two or more titre values that do not differ by more than 0.20cm3 .This called concordancy
Rough titre may be used in averaging if it is within the concordant values.
Recording in titration
Slide 36
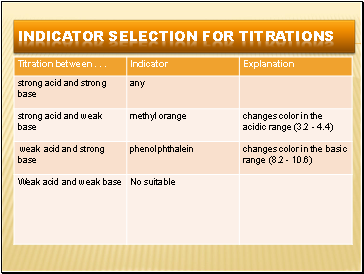
Indicator Selection for Titrations
Slide 37
Titration Calculations
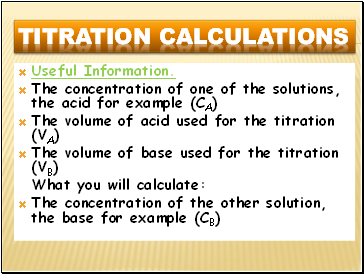
Useful Information.
The concentration of one of the solutions, the acid for example (CA)
The volume of acid used for the titration (VA)
The volume of base used for the titration (VB)
What you will calculate:
The concentration of the other solution, the base for example (CB)
Slide 38
Details of the theory behind the calculations
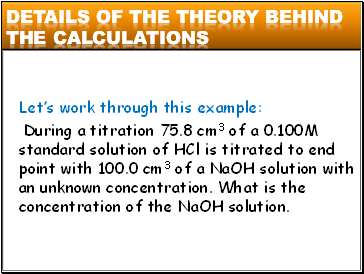
Letís work through this example:
During a titration 75.8 cm3 of a 0.100M standard solution of HCl is titrated to end point with 100.0 cm3 of a NaOH solution with an unknown concentration. What is the concentration of the NaOH solution.
Slide 39
The theory
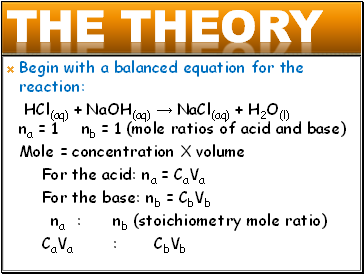
Begin with a balanced equation for the reaction:
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) na = 1 nb = 1 (mole ratios of acid and base)
Mole = concentration X volume
For the acid: na = CaVa
For the base: nb = CbVb
na : nb (stoichiometry mole ratio)
CaVa : CbVb
Slide 40
The Theory
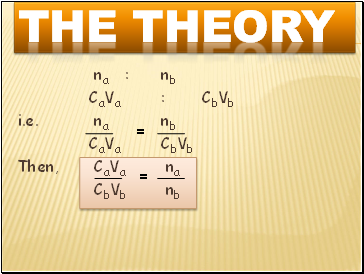
na : nb
CaVa : CbVb
i.e. na nb
CaVa CbVb
Then, CaVa na
CbVb nb
=
=
Slide 41
Tips on solving the problem
Convert the given conc. (base/acid) mol/dm3 to mol/given vol(base/acid).
If the conc. Is given in g/dm3, first convert to . mol/dm3 then to mol/given vol(base/acid).
Use the mole ratio and mol/given vol(base/acid)., get the mol/given vol.(acid/base).
Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of terms
- Relationship between molar conc & mass conc
- Concentration of solution
- Solved problems involved concentration
- Alternatively
- Principle of dillution (dillution factor)
- Acid-Base Titrations
- During the titration
- At the end point
- Volumetric apparatus
- Titration Procedure
- How do you know when you are reaching the endpoint?
- Precautions during titration
- Recording in titration
- Indicator Selection for Titrations
- Titration Calculations
- Details of the theory behind the calculations
- The theory
- Tips on solving the problem
- Letís solve it together
Last added presentations
- Friction
- Space Radiation
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Madame Marie Curie
- Newtonís laws of motion
- Buoyancy
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms