Chemical BondsPage
2
2
Slide 9
The periodic table
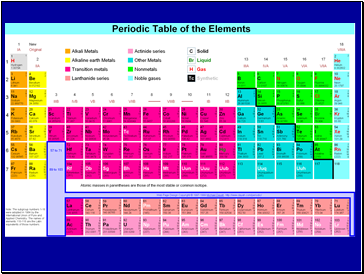
By the late 1800’s it was realized that elements could be grouped by similar chemical properties and that the chemical and physical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers – PERIODIC LAW.
The arrangements of the elements in order of increasing atomic number, with elements having similar properties placed in a vertical column, is called the PERIODIC TABLE.
Slide 10
Slide 11
Slide 12
Columns are called GROUPS (FAMILIES) and rows are called PERIODS.
Elements in a group have similar chemical and physical properties.
Slide 13
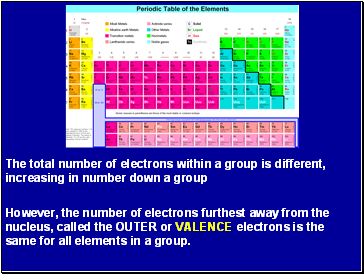
The total number of electrons within a group is different, increasing in number down a group
However, the number of electrons furthest away from the nucleus, called the OUTER or VALENCE electrons is the same for all elements in a group.
Slide 14
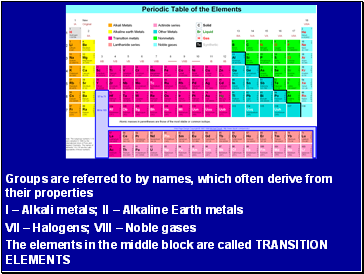
Groups are referred to by names, which often derive from their properties
I – Alkali metals; II – Alkaline Earth metals
VII – Halogens; VIII – Noble gases
The elements in the middle block are called TRANSITION ELEMENTS
Slide 15
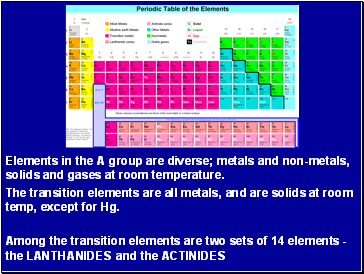
Elements in the A group are diverse; metals and non-metals, solids and gases at room temperature.
The transition elements are all metals, and are solids at room temp, except for Hg.
Among the transition elements are two sets of 14 elements - the LANTHANIDES and the ACTINIDES
Slide 16
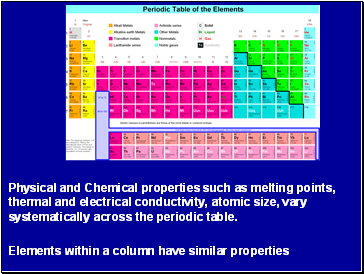
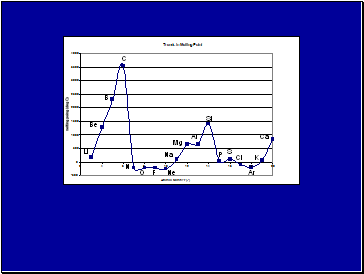
Physical and Chemical properties such as melting points, thermal and electrical conductivity, atomic size, vary systematically across the periodic table.
Elements within a column have similar properties
Slide 17
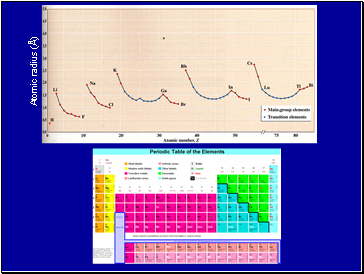
Atomic radius (Å)
Slide 18
Slide 19
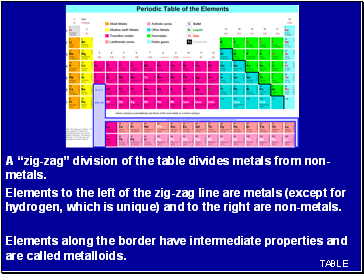
A “zig-zag” division of the table divides metals from non-metals.
Elements to the left of the zig-zag line are metals (except for hydrogen, which is unique) and to the right are non-metals.
Elements along the border have intermediate properties and are called metalloids.
TABLE
Slide 20
Electronegativity
Contents
Last added presentations
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Motion
- Newton’s third law of motion
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Health Physics
- Friction
- Madame Marie Curie