Chemical BondsPage
3
3
The type of bond formed between a pair of atoms is determined by the ability of the atoms to attract electrons from the other.
A positively charged ion (CATION) is formed when an atom looses one or more electrons and a negatively charged ion (ANION) is formed when an atom accepts one or more electrons.
For a free, isolated atom its ability to loose an electron is measured by its IONIZATION ENERGY, while the ability to gain an electron is measured by its ELECTRON AFFINITY
Slide 21
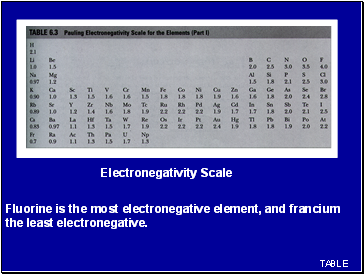
The average of these two properties for isolated atoms define the atom’s ELECTRONEGATIVITY which measures the tendency of one atom to attract electrons from another atom to which it is bonded.
For example, Metallic elements loose electrons (to form positive ions) more readily than non-metallic elements
Metallic elements are hence referred to as being more ELECTROPOSITIVE that non-metals.
Non-metals are more ELECTRONEGATIVE compared to metals
Slide 22
The periodic table’s arrangement results in a separation of metals from non-metals (metallic nature increasing to the left and down, non metallic increasing right and up).
This allows for a comparative scale for the electronegativity of elements.
TABLE
Slide 23
Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and francium the least electronegative.
TABLE
Slide 24
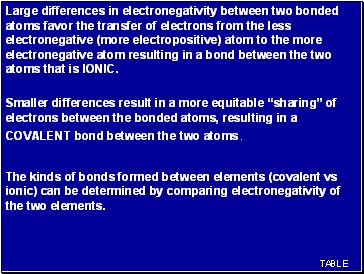
Large differences in electronegativity between two bonded atoms favor the transfer of electrons from the less electronegative (more electropositive) atom to the more electronegative atom resulting in a bond between the two atoms that is IONIC.
Smaller differences result in a more equitable “sharing” of electrons between the bonded atoms, resulting in a COVALENT bond between the two atoms.
The kinds of bonds formed between elements (covalent vs ionic) can be determined by comparing electronegativity of the two elements.
TABLE
Slide 25
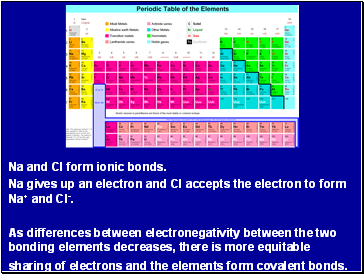
Na and Cl form ionic bonds.
Na gives up an electron and Cl accepts the electron to form Na+ and Cl-.
As differences between electronegativity between the two bonding elements decreases, there is more equitable sharing of electrons and the elements form covalent bonds.
Slide 26
Based on the position of elements in the periodic table, we can determine the kind of bond formed
Generally:
Nonmetallic element + nonmetallic element Molecular compound
Molecular compounds are typically gases, liquids, or low melting point solids and are characteristically poor conductors. Examples are H2O, CH4, NH3.
Contents
Last added presentations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Solar Energy
- Madame Marie Curie
- Soil and Plant Nutrition