Acids and Bases. Arrhenius Acids and BasesPage
1
1
Slide 1

ACIDS AND BASES
CHAPTER 15
Slide 2
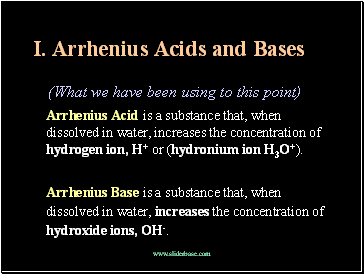
Arrhenius Acids and Bases
(What we have been using to this point)
Arrhenius Acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydrogen ion, H+ or (hydronium ion H3O+).
Arrhenius Base is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydroxide ions, OH-.
Slide 3
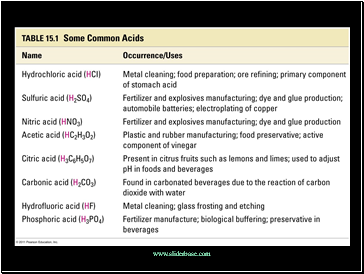
Slide 4
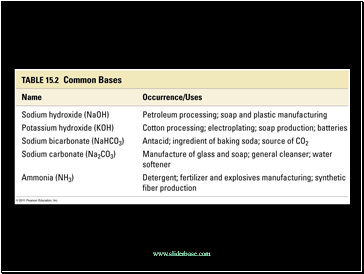
Slide 5
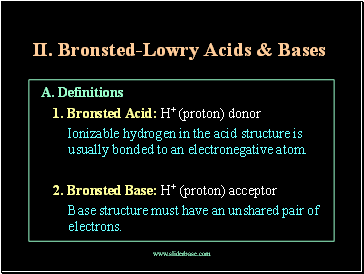
Bronsted-Lowry Acids & Bases
A. Definitions
1. Bronsted Acid: H+ (proton) donor
Ionizable hydrogen in the acid structure is usually bonded to an electronegative atom.
2. Bronsted Base: H+ (proton) acceptor
Base structure must have an unshared pair of electrons.
Slide 6
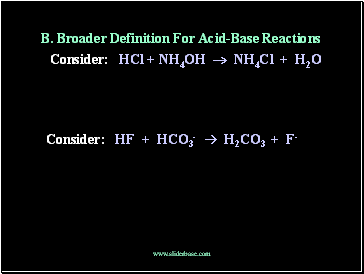
B. Broader Definition For Acid-Base Reactions
Consider: HCl + NH4OH NH4Cl + H2O
Consider: HF + HCO3- H2CO3 + F-
Slide 7
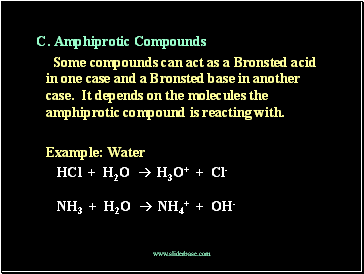
C. Amphiprotic Compounds
Some compounds can act as a Bronsted acid in one case and a Bronsted base in another case. It depends on the molecules the amphiprotic compound is reacting with.
Example: Water
HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl-
NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH-
Slide 8

D. Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
A conjugate acid-base pair consists of two species in an acid-base reaction, one acid and one base, that differ by the loss or gain of a proton.
Conjugate acid- species formed when a base has accepted a proton.
Conjugate base- species formed when an acid has donated or removed a proton.
Example: Acetic Acid
CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO- + H+
CH3COOH + H2O ⇌ CH3COO- + H3O+
Slide 9
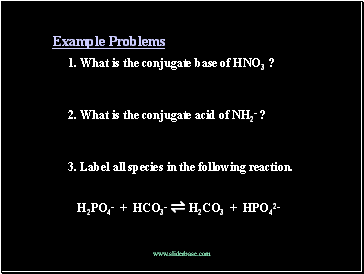
Example Problems
1. What is the conjugate base of HNO3 ?
2. What is the conjugate acid of NH2- ?
3. Label all species in the following reaction.
H2PO4- + HCO3- ⇌ H2CO3 + HPO42-
Slide 10
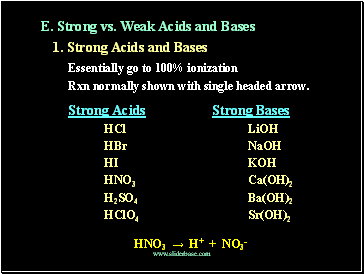
E. Strong vs. Weak Acids and Bases
1. Strong Acids and Bases
Essentially go to 100% ionization
Rxn normally shown with single headed arrow.
Strong Acids Strong Bases
HCl LiOH
HBr NaOH
HI KOH
Contents
- Arrhenius Acids and Bases
- Bronsted-Lowry Acids & Bases
- Self-Ionization of Water
- pH Scale
- Strong Acids and Bases
- Weak Acid Equilibrium Rxns
- Weak Base Equilibrium Rxns
- Relationship of Ka and Kb
- Acid-Base Reactions of Salts (Ions as Acids and Bases)
- Lewis Acids and Bases
- Acid Rain
Last added presentations
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Gravitation
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Newton's Laws
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
