Acids and Bases. Arrhenius Acids and BasesPage
5
5
2. Show the chemical reaction to which Ka applies for H2PO41-
4. Determine the Kb value for HPO42-.
5. Which direction is the reaction favored?
Slide 38
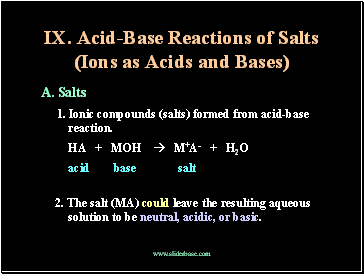
Acid-Base Reactions of Salts (Ions as Acids and Bases)
A. Salts
1. Ionic compounds (salts) formed from acid-base reaction.
HA + MOH M+A- + H2O
acid base salt
2. The salt (MA) could leave the resulting aqueous solution to be neutral, acidic, or basic.
Slide 39

B. Hydrolysis of Salts
Salts may react with water (hydrolysis reaction involving the splitting of a water molecule) to produce acidic or basic solutions.
For hypothetical ionic compound MA, consisting of
Mx+ cation and Ax- anion, consider possible
hydrolysis reactions and possible consequences:
Mx+ + H2O M(OH)(x-1)+ + H+ acidic solution
Ax- + H2O HA(x+1)- + OH- basic solution
If both cation and anion hydrolyze, compare Ka and Kb
Slide 40

C. Predicting If Hydrolysis Occurs
1. Write the hypothetical hydrolysis rxns for salt.
(one for cation and one for anion)
2. Look at the hypothetical hydrolysis products.
3. If a strong acid or strong base was hypothetically
produced, these hydrolysis reactions DO NOT
occur. No acid or base properties upon
hydrolysis. Recall Table of Strong Acids and Bases
4. If a weak acid or base was produced, these hydrolysis reactions DO occur and produce acid or base properties. For hydrolysis products:
H+ : acidic OH- : Basic
Slide 41

D. Example Problems
Will an aqueous solution of the salt be acidic,
basic, or neutral?
1) NaCl
2) NH4Cl
3) NH4CN
Slide 42

Cumulative Example Problem
The cyanate ion, OCN-, is a weak base. The Ka for HOCN (cyanic acid) is 3.4 x 10-8. Calculate the pH of a 0.200 M solution of NaOCN.
Slide 43
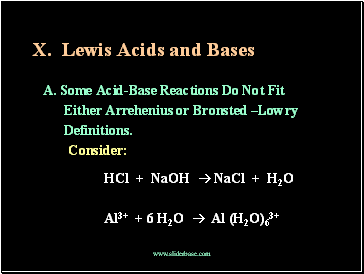
Lewis Acids and Bases
A. Some Acid-Base Reactions Do Not Fit
Either Arrehenius or Bronsted –Lowry
Definitions.
Consider:
HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O
Al3+ + 6 H2O Al (H2O)63+
Slide 44

B. Lewis Acids and Bases
1. Lewis Acid: electron pair acceptor
(Accepts a pair of electrons to form a new bond)
** Usually has an incomplete octet of electrons
2. Lewis Base: electron pair donor
(Donates a pair of electrons to form a new bond)
Contents
- Arrhenius Acids and Bases
- Bronsted-Lowry Acids & Bases
- Self-Ionization of Water
- pH Scale
- Strong Acids and Bases
- Weak Acid Equilibrium Rxns
- Weak Base Equilibrium Rxns
- Relationship of Ka and Kb
- Acid-Base Reactions of Salts (Ions as Acids and Bases)
- Lewis Acids and Bases
- Acid Rain
Last added presentations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Space Radiation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Solar Energy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Health Physics
