Atomic Structure and PeriodicityPage
5
5
The five d orbital shapes are shown below. The d orbitals have two different fundamental shapes.
The Boundary Surfaces of All of the 3d Orbitals
Slide 31
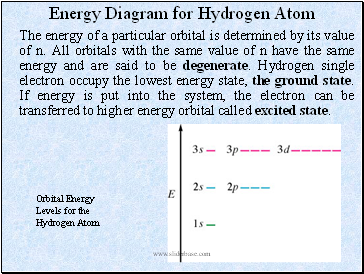
Energy Diagram for Hydrogen Atom
The energy of a particular orbital is determined by its value of n. All orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy and are said to be degenerate. Hydrogen single electron occupy the lowest energy state, the ground state. If energy is put into the system, the electron can be transferred to higher energy orbital called excited state. Orbital Energy Levels for the Hydrogen Atom
Slide 32
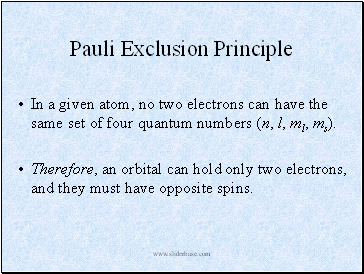
Pauli Exclusion Principle
In a given atom, no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms).
Therefore, an orbital can hold only two electrons, and they must have opposite spins.
Slide 33
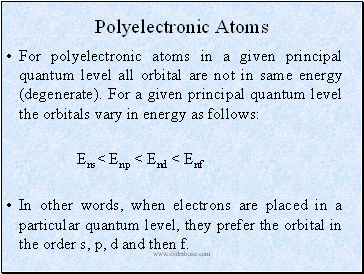
Polyelectronic Atoms
For polyelectronic atoms in a given principal quantum level all orbital are not in same energy (degenerate). For a given principal quantum level the orbitals vary in energy as follows:
Ens< Enp < End < Enf
In other words, when electrons are placed in a particular quantum level, they prefer the orbital in the order s, p, d and then f.
Slide 34
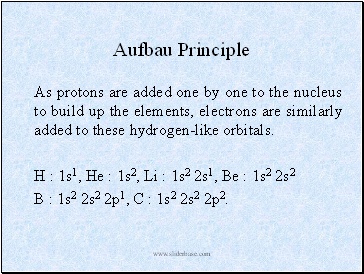
Aufbau Principle
As protons are added one by one to the nucleus to build up the elements, electrons are similarly added to these hydrogen-like orbitals.
H : 1s1, He : 1s2, Li : 1s2 2s1, Be : 1s2 2s2
B : 1s2 2s2 2p1, C : 1s2 2s2 2p2.
Slide 35
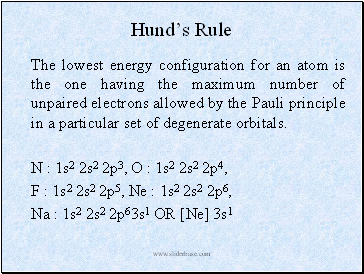
Hundís Rule
The lowest energy configuration for an atom is the one having the maximum number of unpaired electrons allowed by the Pauli principle in a particular set of degenerate orbitals.
N : 1s2 2s2 2p3, O : 1s2 2s2 2p4,
F : 1s2 2s2 2p5, Ne : 1s2 2s2 2p6,
Na : 1s2 2s2 2p63s1 OR [Ne] 3s1
Slide 36
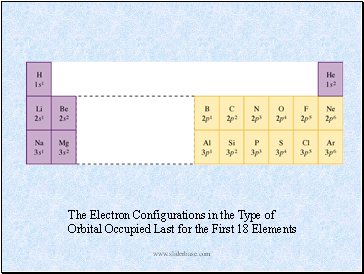
The Electron Configurations in the Type of
Orbital Occupied Last for the First 18 Elements
Slide 37
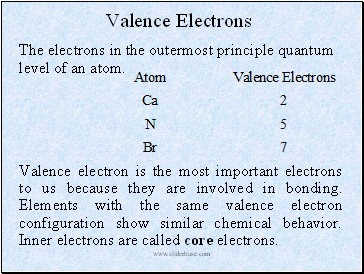
Valence Electrons
The electrons in the outermost principle quantum level of an atom.
Valence electron is the most important electrons to us because they are involved in bonding. Elements with the same valence electron configuration show similar chemical behavior. Inner electrons are called core electrons.
Slide 38
Contents
- Waves
- Planckís Constant
- Energy and Mass
- Wavelength and Mass
- Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen
- The Bohr Model
- Quantum Mechanics
- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
- Quantum Numbers (QN)
- Orbital Shapes and Energies
- Representation of p orbitals
- Representation d orbitals
- Energy Diagram for Hydrogen Atom
- Pauli Exclusion Principle
- Polyelectronic Atoms
- Aufbau Principle
- Hundís Rule
- Valence Electrons
- Broad Periodic Table Classifications
- Ionization Energy
- Periodic Trends
- Electron Affinity
- Periodic Trends
- Information Contained in the Periodic Table
Last added presentations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Newtonís third law of motion
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Space Radiation
- Newtonís laws of motion
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy