The Immune SystemPage
3
3
About 30 proteins make up the complement system, which causes lysis of invading cells and helps trigger inflammation.
Slide 16
Inflammatory Responses
Following an injury, mast cells release histamine, which promotes changes in blood vessels; this is part of the inflammatory response.
These changes increase local blood supply and allow more phagocytes and antimicrobial proteins to enter tissues.
Pus = a fluid rich in white blood cells, dead microbes, and cell debris, accumulates at the site of inflammation.
Slide 17
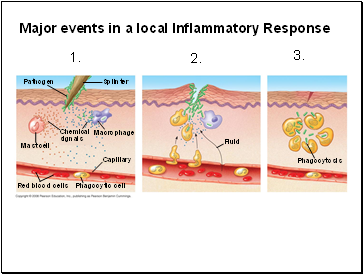
Major events in a local Inflammatory Response
Pathogen
Splinter
Macrophage
Mast cell
Chemical
signals
Capillary
Phagocytic cell
Red blood cells
Fluid
Phagocytosis
1.
2.
3.
Slide 18
Inflammation can be either local or systemic (throughout the body).
Fever is a systemic inflammatory response triggered by pyrogens released by macrophages, and toxins from pathogens.
Septic shock is a life-threatening condition caused by an overwhelming inflammatory response.
Slide 19
Natural Killer Cells
All body cells (except red blood cells) have a class I MHC protein on their surface.
MHC = Major Histocompatibility Complex , part of the extracellular matrix.
Class II MHC protein molecules are found on specialized cells
Cancerous or infected cells no longer express this MHC protein; natural killer (NK) cells attack these damaged cells.
Slide 20
Innate Immune System Evasion by Pathogens
Some pathogens avoid destruction by modifying their surface to prevent recognition or by resisting breakdown following phagocytosis.
Tuberculosis (TB) is one such disease and kills more than a million people a year.
Slide 21
In Acquired Immunity, lymphocyte receptors provide pathogen-specific recognition
White blood cells called lymphocytes recognize and respond to antigens, foreign molecules.
Lymphocytes that mature in the thymus above the heart are called T cells, and those that mature in bone marrow are called B cells.
Lymphocytes contribute to immunological memory, an enhanced response to a foreign molecule encountered previously.
Cytokines are secreted by macrophages and dendritic cells to recruit and activate lymphocytes.
Slide 22
Acquired Immunity = Active Immunity: Specific
Contents
- Reconnaissance, Recognition, and Response
- Innate Immunity of Invertebrates
- Innate Immunity Defenses of Vertebrates
- Innate Immune System Evasion by Pathogens
- In Acquired Immunity, lymphocyte receptors provide pathogen-specific recognition
- Lymphocyte Development
- Acquired immunity defends against infection of body cells and fluids
- Helper T Cells: Respond to Nearly All Antigens
- Cytotoxic T Cells: A Response to Infected Cells
- B Cells: A Response to Extracellular Pathogens
- Active Immunization
- Passive Immunity
- Immune Rejection
- Disruption in immune system function can elicit or exacerbate disease
- Acquired Immune System Evasion by Pathogens
- Cancer and Immunity
Last added presentations
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Newton's Laws
- Upcoming Classes
- Sound
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Mechanics Lecture
- Radiation