The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesPage
5
5
Slide 39
Fats separate from water because water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and exclude the fats
In a fat, three fatty acids are joined to glycerol by an ester linkage, creating a triacylglycerol, or triglyceride
Slide 40
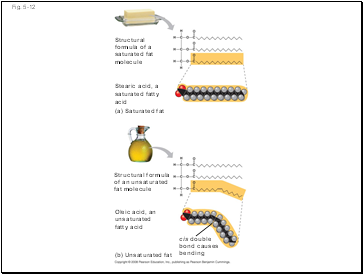
Fatty acids vary in length (number of carbons) and in the number and locations of double bonds
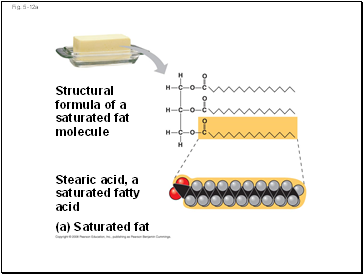
Saturated fatty acids have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds
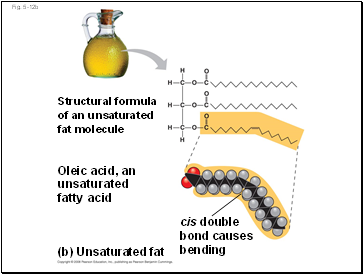
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds
Animation: Fats
Slide 41
Fig. 5-12
Structural
formula of a
saturated fat
molecule
Stearic acid, a
saturated fatty
acid
(a) Saturated fat
Structural formula
of an unsaturated
fat molecule
Oleic acid, an
unsaturated
fatty acid
(b) Unsaturated fat
cis double
bond causes
bending
Slide 42
Fig. 5-12a
(a)
Saturated fat
Structural
formula of a
saturated fat
molecule
Stearic acid, a
saturated fatty
acid
Slide 43
Fig. 5-12b
(b)
Unsaturated fat
Structural formula
of an unsaturated
fat molecule
Oleic acid, an
unsaturated
fatty acid
cis double
bond causes
bending
Slide 44
Fats made from saturated fatty acids are called saturated fats, and are solid at room temperature
Most animal fats are saturated
Fats made from unsaturated fatty acids are called unsaturated fats or oils, and are liquid at room temperature
Plant fats and fish fats are usually unsaturated
Slide 45
A diet rich in saturated fats may contribute to cardiovascular disease through plaque deposits
Hydrogenation is the process of converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding hydrogen
Hydrogenating vegetable oils also creates unsaturated fats with trans double bonds
These trans fats may contribute more than saturated fats to cardiovascular disease
Slide 46
The major function of fats is energy storage
Humans and other mammals store their fat in adipose cells
Adipose tissue also cushions vital organs and insulates the body
Slide 47
Phospholipids
In a phospholipid, two fatty acids and a phosphate group are attached to glycerol
Contents
- The Molecules of Life
- The Synthesis and Breakdown of Polymers
- The Diversity of Polymers
- Sugars
- Polysaccharides
- Fats
- Phospholipids
- Steroids
- Polypeptides
- Protein Structure and Function
- The Roles of Nucleic Acids
- The Structure of Nucleic Acids
- The DNA Double Helix
- DNA and Proteins as Tape Measures of Evolution
- The Theme of Emergent Properties in the Chemistry of Life: A Review
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton's laws of motion
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Madame Marie Curie
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants