The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesPage
13
13
group
Sugar
(pentose)
(b) Nucleotide
(a) Polynucleotide, or nucleic acid
3 end
3C
3C
5C
5C
Nitrogenous bases
Pyrimidines
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T, in DNA)
Uracil (U, in RNA)
Purines
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Sugars
Deoxyribose (in DNA)
Ribose (in RNA)
(c) Nucleoside components: sugars
Slide 109
Fig. 5-27ab
5' end
5'C
3'C
5'C
3'C
3' end
(a) Polynucleotide, or nucleic acid
(b) Nucleotide
Nucleoside
Nitrogenous
base
3'C
5'C
Phosphate
group
Sugar
(pentose)
Slide 110
Fig. 5-27c-1
(c) Nucleoside components: nitrogenous bases
Purines
Guanine (G)
Adenine (A)
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T, in DNA)
Uracil (U, in RNA)
Nitrogenous bases
Pyrimidines
Slide 111
Fig. 5-27c-2
Ribose (in RNA)
Deoxyribose (in DNA)
Sugars
(c) Nucleoside components: sugars
Slide 112
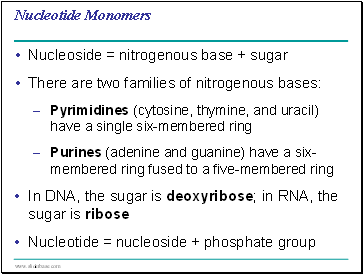
Nucleotide Monomers
Nucleoside = nitrogenous base + sugar
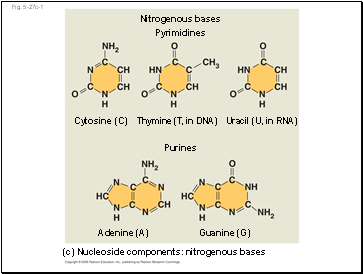
There are two families of nitrogenous bases:
Pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil) have a single six-membered ring
Purines (adenine and guanine) have a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring
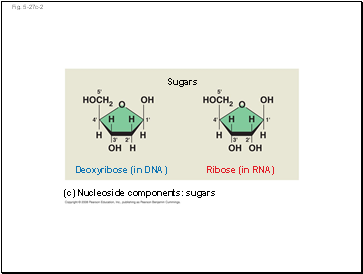
In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose; in RNA, the sugar is ribose
Nucleotide = nucleoside + phosphate group
Slide 113
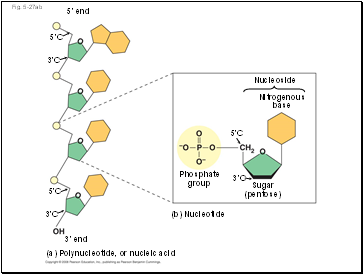
Nucleotide Polymers
Nucleotide polymers are linked together to build a polynucleotide
Adjacent nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds that form between the –OH group on the 3 carbon of one nucleotide and the phosphate on the 5 carbon on the next
These links create a backbone of sugar-phosphate units with nitrogenous bases as appendages
The sequence of bases along a DNA or mRNA polymer is unique for each gene
Slide 114
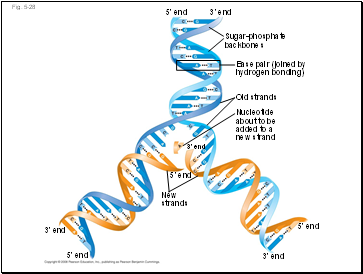
The DNA Double Helix
A DNA molecule has two polynucleotides spiraling around an imaginary axis, forming a double helix
In the DNA double helix, the two backbones run in opposite 5 → 3 directions from each other, an arrangement referred to as antiparallel
One DNA molecule includes many genes
The nitrogenous bases in DNA pair up and form hydrogen bonds: adenine (A) always with thymine (T), and guanine (G) always with cytosine (C)
Slide 115
Contents
- The Molecules of Life
- The Synthesis and Breakdown of Polymers
- The Diversity of Polymers
- Sugars
- Polysaccharides
- Fats
- Phospholipids
- Steroids
- Polypeptides
- Protein Structure and Function
- The Roles of Nucleic Acids
- The Structure of Nucleic Acids
- The DNA Double Helix
- DNA and Proteins as Tape Measures of Evolution
- The Theme of Emergent Properties in the Chemistry of Life: A Review
Last added presentations
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy