Reaction TypesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Reaction Types
Slide 2
Combination (Synthesis) Reactions
Two or more substances combine to form a new compound.
A + X AX
Reaction of elements with oxygen and sulfur
Reactions of metals with Halogens
Synthesis Reactions with Oxides
There are others not covered here!
Slide 3
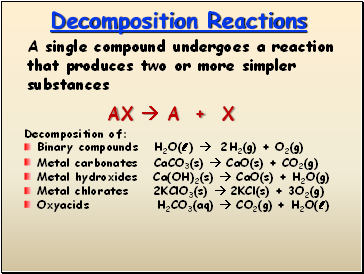
Decomposition Reactions
A single compound undergoes a reaction that produces two or more simpler substances
Decomposition of:
Binary compounds H2O(l ) 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Metal carbonates CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Metal hydroxides Ca(OH)2(s) CaO(s) + H2O(g)
Metal chlorates 2KClO3(s) 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g)
Oxyacids H2CO3(aq) CO2(g) + H2O(l )
AX A + X
Slide 4
Single Replacement Reactions
Replacement of:
Metals by another metal
Hydrogen in water by a metal
Hydrogen in an acid by a metal
Halogens by more active halogens
A + BX AX + B
BX + Y BY + X
Slide 5
The Activity Series of the Metals
Lithium
Potassium
Calcium
Sodium
Magnesium
Aluminum
Zinc
Chromium
Iron
Nickel
Lead
Hydrogen
Bismuth
Copper
Mercury
Silver
Platinum
Gold
Metals can replace other metals provided that they are above the metal that they are trying to replace
Metals above hydrogen can replace hydrogen in acids.
Metals from sodium upward can replace hydrogen in water
Slide 6
The Activity Series of the Halogens
Fluorine
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
Halogens can replace other halogens in compounds, provided
that they are above the halogen that they are trying to replace.
2NaCl(s) + F2(g)
2NaF(s) + Cl2(g)
MgCl2(s) + Br2(g)
???
No Reaction
???
Slide 7
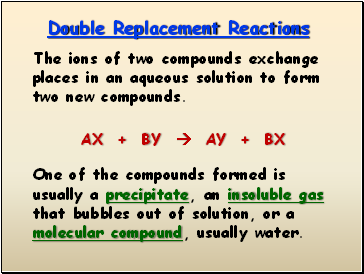
Double Replacement Reactions
The ions of two compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds.
AX + BY AY + BX
One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of solution, or a molecular compound, usually water.
Slide 8
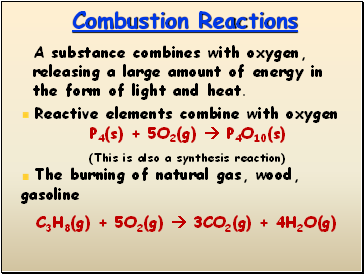
Combustion Reactions
A substance combines with oxygen, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of light and heat.
1 2
Contents
- Combination (Synthesis) Reactions
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Replacement Reactions
- The Activity Series of the Metals
- The Activity Series of the Halogens
- Double Replacement Reactions
- Combustion Reactions
Last added presentations
- Upcoming Classes
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Newton's Laws
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Motion