The Moon Geology, Exploration, OriginPage
1
1
Slide 1
Solar System Planets: The Earth + Moon
•Moon
- Atmosphere
- Surface/Geological Features/Moon Rocks
- Interior
- Origin
II. Mercury
- Basic Facts
- Exploration
- Cratering
Slide 2
The Moon has no atmosphere
• allows us to see the surface with fine detail
• escape speed is too low on the Moon
- all gas molecules can escape!
• no atmospheric pressure means that water can not exist in liquid form
- only in solid or vapor
• temperature variations – extreme!
- day T = 403 K = 266 F
- night T = 93 K = -292 F
- day/night are each 2 weeks long!
• no weathering of the surface by water, storm
• no protection from high energy solar particles, cosmic rays
Slide 3
Lunar Geological Features
•Craters
• ~30,000 visible with small telescopes from Earth
• millions visible from lunar orbiting satellites
• origin: interplanetary debris
•sizes: largest 100’s km
across a result of fast
moving impact rocks
of only a few km’s across!
•large craters often
produce “central peak”
craters
Slide 4
Lunar Geological Features
2. Lunar “Maria” - dark, smooth regions
• first thought to actually be wet areas (before we knew Moon had no atmosphere)
• now believed to be smoother, younger (fewer craters) surfaces
• idea is that impacts created large basin and then lava flowed over surface
• relatively ‘low’ compared to highlands on moon; 2-5 km below other parts
• rough mountain ranges surrounding ‘maria’ suggest large impact originally
• evidence for ‘flows’ (lava?) along the smooth maria
Slide 5
Lunar Geological Features
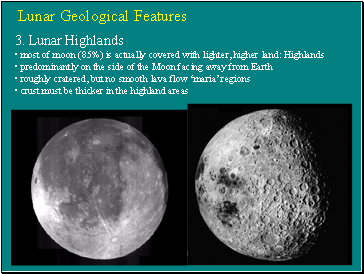
3. Lunar Highlands
• most of moon (85%) is actually covered with lighter, higher land: Highlands
• predominantly on the side of the Moon facing away from Earth
• roughly cratered, but no smooth lava flow ‘maria’ regions
• crust must be thicker in the highland areas
Slide 6
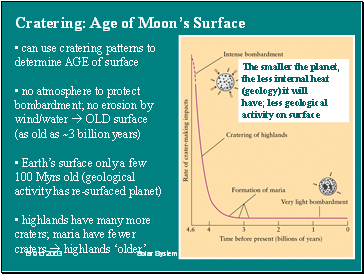
Cratering: Age of Moon’s Surface
• can use cratering patterns to determine AGE of surface
• no atmosphere to protect
bombardment; no erosion by
wind/water à OLD surface
(as old as ~3 billion years)
• Earth’s surface only a few
100 Myrs old (geological activity has re-surfaced planet)
• highlands have many more craters; maria have fewer
craters à highlands ‘older’
Contents
- Solar System Planets: The Earth + Moon
- The Moon has no atmosphere
- Lunar Geological Features
- Cratering: Age of Moon’s Surface
- A Brief History of Lunar Exploration
- Highlights from Apollo 11 mission
- First steps on the Moon
- Mars Express: Radar Experiment
- Recent Lunar Exploration
- Moon Rocks: Sampling the Surface of the Moon
- Moonquakes: Studying the Moon’s Interior
- Moon’s interior structure
- Theories for Origin of Moon
- Computer Simulation of Formation of Moon
Last added presentations
- Motion
- Health Physics
- Friction
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Gravitation
- Radiation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy