Cell membrane transportPage
1
1
Slide 1
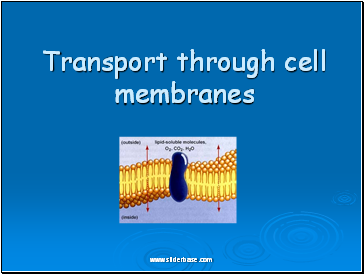
Transport through cell membranes
Slide 2
Transport through cell membranes
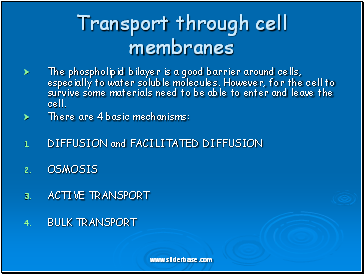
The phospholipid bilayer is a good barrier around cells, especially to water soluble molecules. However, for the cell to survive some materials need to be able to enter and leave the cell.
There are 4 basic mechanisms:
DIFFUSION and FACILITATED DIFFUSION
OSMOSIS
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
BULK TRANSPORT
Slide 3
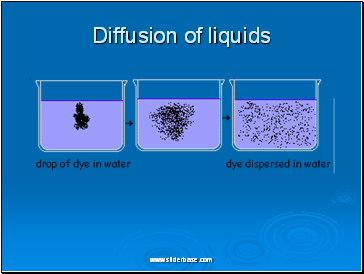
Diffusion of liquids
Slide 4
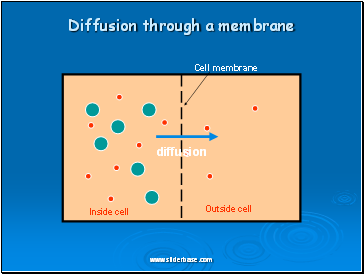
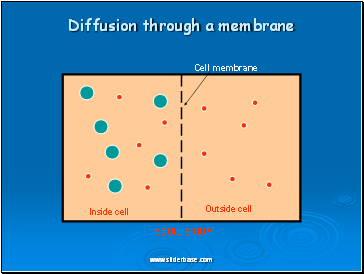
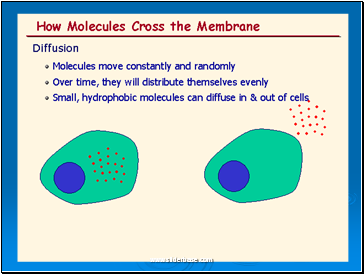
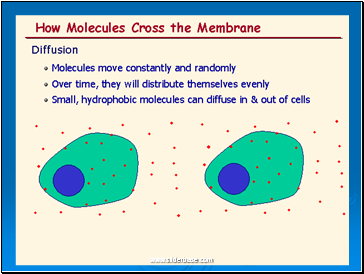
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules (or ions) from a region of their high concentration to a region of their lower concentration. The molecules move down a concentration gradient. Molecules have kinetic energy, which makes them move about randomly. As a result of diffusion molecules reach an equilibrium where they are evenly spread out. This is when there is no net movement of molecules from either side.
Slide 5
DIFFUSION
Diffusion is a PASSIVE process which means no energy is used to make the molecules move, they have a natural kinetic energy.
Slide 6
Diffusion of Bromine
Slide 7
Diffusion of Bromine
Slide 8
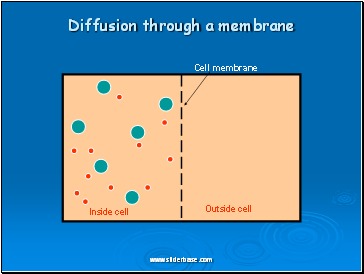
Diffusion through a membrane
Cell membrane
Inside cell
Outside cell
Slide 9
Diffusion through a membrane
Cell membrane
Inside cell
Outside cell
diffusion
Slide 10
Diffusion through a membrane
Cell membrane
Inside cell
Outside cell
EQUILIBRIUM
Slide 11
Slide 12
Slide 13
What determines the rate of diffusion? There 4 factors:
The steepness of the concentration gradient. The bigger the difference between the two sides of the membrane the quicker the rate of diffusion.
Temperature. Higher temperatures give molecules or ions more kinetic energy. Molecules move around faster, so diffusion is faster.
The surface area. The greater the surface area the faster the diffusion can take place. This is because the more molecules or ions can cross the membrane at any one moment.
Contents
- Transport through cell membranes
- Diffusion of liquids
- Diffusion of Bromine
- What determines the rate of diffusion? There 4 factors:
- Facilitated diffusion
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Exocytosis
- Receptor Proteins
- Vesicle-mediated transport
- Cell Membrane - Function – Endocytosis
Last added presentations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Sound
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Waves & Sound
- Space Radiation