Population EcologyPage
4
4
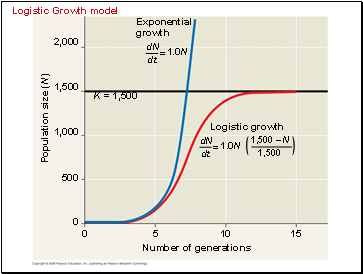
The logistic model of population growth produces a sigmoid (S-shaped) curve.
Slide 23
Logistic Growth model
2,000
1,500
1,000
500
0
0
5
10
15
Number of generations
Population size (N)
Exponential
growth
1.0N
=
dN
dt
1.0N
=
dN
dt
K = 1,500
Logistic growth
1,500 – N
1,500
Slide 24
The Logistic Model and Real Populations
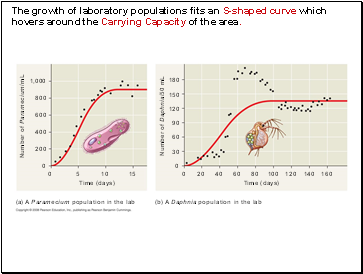
The growth of laboratory populations of paramecia fits an S-shaped curve.
These organisms are grown in a constant environment lacking predators and competitors.
Some populations overshoot K before settling down to a relatively stable density.
Slide 25
The growth of laboratory populations fits an S-shaped curve which hovers around the Carrying Capacity of the area.
1,000
800
600
400
200
0
0
5
10
15
Time (days)
Number of Paramecium/mL
Number of Daphnia/50 mL
0
30
60
90
180
150
120
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Time (days)
(b) A Daphnia population in the lab
(a) A Paramecium population in the lab
Slide 26
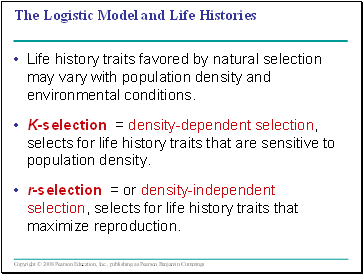
The Logistic Model and Life Histories
Life history traits favored by natural selection may vary with population density and environmental conditions.
K-selection = density-dependent selection, selects for life history traits that are sensitive to population density.
r-selection = or density-independent selection, selects for life history traits that maximize reproduction.
Slide 27
Many factors that regulate population growth are density dependent
There are two general questions about regulation of population growth:
What environmental factors stop a population from growing indefinitely?
Why do some populations show radical fluctuations in size over time, while others remain stable?
Slide 28
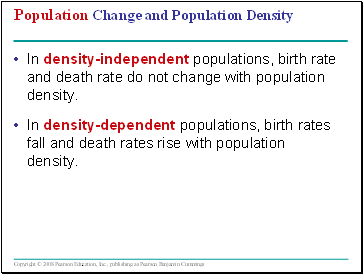
Population Change and Population Density
In density-independent populations, birth rate and death rate do not change with population density.
In density-dependent populations, birth rates fall and death rates rise with population density.
Slide 29
Density-Dependent Population Regulation
Density-dependent birth and death rates are an example of negative feedback that regulates population growth.
Contents
- Population ecology
- Dynamic biological processes influence population density, dispersion, and demographics
- Demographics
- Life history traits are products of natural selection
- Evolution and Life History Diversity
- “Trade-offs” and Life Histories
- The exponential model describes population growth in an idealized, unlimited environment
- Exponential Growth
- The logistic model describes how a population grows more slowly as it nears its carrying capacity
- The Logistic Model and Real Populations
- The Logistic Model and Life Histories
- Many factors that regulate population growth are density dependent
- Population Change and Population Density
- Density-Dependent Population Regulation
- Population Dynamics
- The human population is no longer growing exponentially but is still increasing rapidly
Last added presentations
- Madame Marie Curie
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Newton's laws of motion
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Thermal Energy
- Space Radiation
- Sound